* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Power Transistors
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
History of the transistor wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
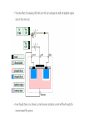
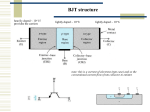
Power Transistors Characteristics Lecture Note 5 The switching speed of modern transistors is much higher than that of Thyristors and are used extensively in dcdc and dc-ac converters. However, their voltage and current ratings are lower than those of thyristors and are therefore used in low to medium power applications. These devices are used a switching devices and are operated in the saturation region resulting in low on-state voltage drop. The transistor remains on so long as the control signal is present. power BJT Low power BJT power MOSFET IGBT power BJT power BJT Vs low Power BJT vertically oriented fourlayer structure of alternating p-type and ntype. maximising the cross-section area results in increase current rating of BJT minimize the on-state resistance reduce the power losses power BJT power BJT Vs low Power BJT doping of emitter layer and collector layer is quite large typically A special layer called the collector drift region (n-) has a light doping level The thickness of the drift region determines the breakdown voltage of the transistor Steady State Characteristics similar to signal level transistors except that the V-I c/cs has Cutoff region, Active region, quasi saturation and hard saturation. Cutoff Region: The C–B and B–E junctions are reverse-biased if VBE<0.7V IB=0A RB ? VB=0V 0V VCE=VCC-ICRC IC= 0 VCE =VCC Steady State Characteristics if VBE>0.7V FB ? Since the potential difference between C and E is zero both junctions are forward-biased Steady State Characteristics if VBE>0.7V FB ? Since the potential at C > at B the collector–base junction is reversed-biased and the base–emitter junction is forward-biased. is the maximum collector to emitter voltage that can be sustained when BJT is carrying substantial collector current. is the collector base breakdown voltage when the emitter is open circuited is the maximum collector to emitter breakdown voltage that can be sustained when base current is zero The transistor is used as a switch therefore it is used only between saturation and cutoff. These values are adjusted in away to make the BJT works as a switch If IB > IBM → IC↑ and VCE falls below VBE. This continues until Collector-Base junction is forward biased and the BJT goes into saturation region. A high value of ODF cannot reduce the CE voltage significantly. VBE increases due to increase base current resulting in increased power loss. Once the transistor is saturated, the CE voltage is not reduced in relation to increase in base current. If the transistor is under driven IB to IBS it may operate in active region, VCE increases resulting in increased power loss. Diode Provide an alternate path a current through the device cannot rise fast to the saturating level of ICS since the inductive nature of the coil opposes any change in current through it. IL Ic For full ON of BJT, Ic reach s to steady state value the coil acts as a short circuit since VL=0, where VL=Ldi/dt What are the states of the diode during Pulses applied? once input pulse drops to zero, the current IC does not fall to zero immediately since inductor will now act as a current source. • Due to internal capacitances the collector current does not respond immediately. • The delay is due to the time required to charge up the BEJ to the forward bias voltage VBE(0.7V). The base current is normally more than that required to saturate the transistor. the higher the ODF, the greater is the amount of extra charge stored in the base. When the input voltage is reversed from V1 to -V2, the reverse current –IB2 helps to discharge the base. Without –IB2 the saturating charge has to be removed entirely due to the storage time ts would be longer. Once the extra charge is removed, BEJ charges to the input voltage –V2 and the base current falls to zero. tf depends on the time constant which is determined by the reverse biased BEJ capacitance. the BJT is a positive temperature coefficient device. As they get warm, hFe increases, causing more current flow. This can lead to thermal runaway. That is why most class A common emitter configurations use an emitter resistor to place limits on the hFe demand, eliminating thermal drift and runaway. A slab of p-type material is formed and two n-regions are formed in the substrate. The source and drain terminals are connected through metallic contacts to n-doped regions, but the absence of a channel between the doped nregions. Construction The source and drain are connected n+ regions. These regions are heavily doped. The gate is not directly connected to the P-type region. There is insulating oxide (Si02) layer between gate metal and p-type layer. The p-type body region forms the channel between drain and source. What happens if we increase VDS while VGS=0V in MOSFET? Effect of VGS in the formation of Inversion layer in MOSFET Increase VDS by keeping VGS as constant Increase VGS; keep VDS constant For little VDS, the drain current increases linearly with VDS, this is called ohmic or linear region. •Additional increase of VDS causes the pinch off point to shift towards the source, dropping the effective length of channel. This effect is called channel length modulation. Volt-Ampere Characteristics of Power MOSFET Alternative Solution Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) The Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) is a minority-carrier device with high input impedance and large bipolar current-carrying capability. Many designers view IGBT as a device with MOS input characteristics and bipolar output characteristic that is a voltage-controlled bipolar device. It combines the best attributes of both Power MOSFET and BJT devices to achieve optimal device characteristics.