* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the korean language morphology
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Comparison (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Untranslatability wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Agglutination wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Morphology (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Russian declension wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
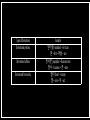
Nathiqa Azira binti Utoh Joehann 1415018 Prof Dr. Nuraihan binti Mat Daud Introduction to Linguistics a branch of linguistics that studies and describes patterns of word formation. The official language of South Korea and North Korea. It was written with adapted Chinese characters called hanja. It is agglutinative in its morphology and SOV in its syntax. Sino-Korean or Hanja-eo refers to the set of words in the Korean language vocabulary that originated from or were influenced by hanja. Sino-Korean words today make up about 60% of the Korean vocabulary. Example: 두부 (dubu), 豆腐 (Dòufu) in Chinese Nouns Pronouns Verbs Copula Adjectives Adverbs Numerals Particles Prenouns Derivational Compounding Borrowing Inflectional • A derivational process is defined as the process of forming a new word on the basis of an existing word. • Derivation stands in contrast to the process of inflection. Types of Derivatives Example Derivational prefixes 맏아들 ‘madadeul’ = First son 맏 = first +아들 = son 장사꾼 ‘jaŋsakkun’ = Business man 장사 = business + 꾼 = doer Derivational suffixes Derivational from verbs 벌이 ‘beori’ = Income 벌 = earn + 이 = act • Compound words are words that add together to make a new word. • It occurs when two or more words are joined together to make them one word. Types of Compounding Example Compound of Nouns: Noun + Noun Noun + Genitive ‘s’ 손목 ‘seon-mok’ = Wrist (hand-neck) 물개 ‘mul-kay’ = Seal (water’s-dog) Compound of Verbs: Noun + Verb (sub+pred) Noun + Verb (obj+pred) 빛나다 ‘pich-nata’ = Shine (light-gives off) 힘스다 ‘him-sseuda’ = Try hard (strength-use) Compound of Adjectives: Noun + Adjective (sub+pred) Reduplicative 배부르다 ‘bae-buleuta’ = Be (stomach-) full 크나크다 ‘keu-na keu-da’ = Be huge Compound of Adverbs: Noun + Noun 오늘날 ‘o-neulnal’ = Nowadays (today-day) • Loanwords are words adopted by the speakers of one language from a different language. A loanword can also be called a borrowing. Back formation Clipping Blending Acronym Types of Borrowing Example Backformation (English) Deletion of Inflectional affix /s/ 하이힐 ‘hai-hileu’ (High heels) Addition of inflectional suffix 하다/했다 (formal) 쇼핑하다 ‘syo-ping-ha-da’ (Shopping) Clipping (English) Front clipping Back clipping 도저 ‘do-jo’ (Bulldozer) 아파트 ‘a-pateu’ (Apartment) Blending 컴푸터피아 ‘kom-pu-to-pi-ah’ (Computer + Phobia) Acronym and Abbreviation 브이아이피 (VIP ) • Inflexion is the modification of a word to express different grammatical categories such as tense, mood, voice, aspect, person, number, gender and case. • Expresses one or more grammatical categories with a prefix, suffix or infix, or another internal modification such as a vowel change. Types of Inflection Example Plural nouns 아기들이 ‘aege-deul’ = Babies Present tense 나는 친구를 만난다 ‘naneun chinggureul mannanda’ = I meet a friend Past tense 나는 친구를 만났다 ‘naneun chinggureul mannatda’ = I met a friend Future tense 나는 먹겠다 ‘naneun meokgetda’ = I will eat