* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download host - microbe relationships and disease
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
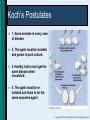
HOST- MICROBE RELATIONSHIPS AND DISEASE PROCESSES CHAPTER 14 Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Symbiotic Relationships Mutualism – Microbe benefits – Host benefits – E. coli in intestine Parasitism – Microbe benefits – Host is damaged – All pathogens Commensalism – Microbe benefits – No effect on host – Corynebacterium in eye Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Host Invasion Contamination – Presence of microbes Infection – Invasion or colonization by microbes Disease – Change away from a normal state of health Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Pathogenicity Determinants Microbial count Virulence / Avirulence Attenuation Virulence Transposition via infection of novel hosts • Rabies vaccine Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Microflora 1014 microbes versus 1013 body cells Colonization Non-sterile areas Sterile areas Resident microflora Transient microflora Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Opportunism Host Defense failure – Immune system – Diabetes – Burn victims Microbes in unusual locations Microflora disturbances Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Koch’s Postulates 1. Same microbe in every case of disease 2. The agent must be isolated and grown in pure culture. 3. Healthy hosts must get the same disease when inoculated. 4. The agent must be reisolated and show to be the same causative agent. Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Exceptions to Koch’s postulates Microbes do not always cause the same disease – Related to portal of entry – e.g. Strep throat, septicemia, flesh eating disease Microbes cannot be cultured in isolation – Viruses, Chlamydia, Rickettsia Many microbes cause the same disease – UTIs, pneumonias, meningitis Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Disease Types Infectious vs. non-infectious Communicable vs. non-communicable Contagious Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Bacterial Pathogenicity Adherence factors permit attachment – Adhesins Damage to Tissues 1. Invasive process directly 2. Enzymes /Toxins 1. Hyaluronidase 2. Coagulase 3. Kinase 3. WBC mediated damage Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Bacterial Toxins Endotoxins Exotoxins Gram negative Gram positive LPS cell wall component Proteins, usually enzymes Fever Potent effects Shock Specialized tissue damage • • • • Released at cell death Hemolysins Leukocidins Neurotoxins Enterotoxins Secreted into bloodstream Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Exotoxin - Hemolysin Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Viral Pathogenicity Cytopathic effects – Cell rupture – Inclusion bodies – Giant cells Latent infections Persistent infections – HBV Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Eukaryotic Pathogen Effects Algae – Toxins Fungi – Toxins/enzymes – Direct damage Protozoa – Direct damage Helminths – Direct damage – Obstruction Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Vocabulary Terms Symptom Subacute disease Sign Latent disease Syndrome Local Sequelae Focal Acute disease Systemic Chronic Disease Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Disease Terminology Bacteremia Primary infection Secondary infection Superinfection Mixed infection Inapparent infection Septicemia Viremia Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Disease stages Incubation Prodromal Invasive (Disease) Decline Convalescence Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Factors influencing Infectious Disease Prevention Health care availability – Drugs – Immunization – Sanitization – Community Health Emergence of new pathogens Social migration/Change Immigration Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.