* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Resistance measurement
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Chirp spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Spectral density wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Time-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
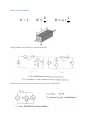
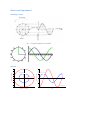
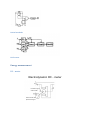
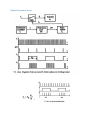
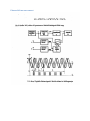
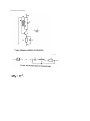
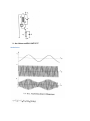
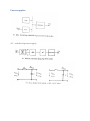
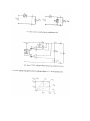
Measurement and instrumentation 2011 Measurement and Instrumentation 2. .................................................................................................... 2 Resistance measurement .................................................................................................................... 2 What is a resistance? ....................................................................................................................... 3 Using Ohms law (indirect measurement)........................................................................................ 3 Direct measurement (multimeters, two wires method) ................................................................. 3 By comparison of measured voltages ............................................................................................. 4 By comparison of measured currents ............................................................................................. 4 Digital multimeter ........................................................................................................................... 4 Wheatstone bridge .......................................................................................................................... 6 Impedance measurement ................................................................................................................... 6 What is the impedance? .................................................................................................................. 7 Rotating vectors .......................................................................................................................... 7 My Sim ......................................................................................................................................... 7 Complex numbers – phasor reprezantation................................................................................ 8 Three voltmeters method ............................................................................................................... 8 Bridge methods ............................................................................................................................... 9 Maxwell – Wien Bridge.............................................................................................................. 10 Wien – Bridge ............................................................................................................................ 10 Resonance method........................................................................................................................ 11 Digital multimeters ........................................................................................................................ 11 Alternative images......................................................................................................................... 11 qualitiy factor ............................................................................................................................ 12 loss factor .................................................................................................................................. 12 Measuring impedances with vector voltmeter ............................................................................. 12 Power measurement ........................................................................................................................ 13 DC – power measurement............................................................................................................. 13 AC – power basics.......................................................................................................................... 14 Active, reactive power, power factor, instantaneous power.................................................... 14 Three voltmeters measurement ............................................................................................... 14 Wattmeters ............................................................................................................................... 14 Electronic methods.................................................................................................................... 14 Digital methods ......................................................................................................................... 15 Hall-sensor ................................................................................................................................. 15 Energy measurement ........................................................................................................................ 15 DC – meter..................................................................................................................................... 15 Using by electromagnetic induction.............................................................................................. 16 Electronic energy meters .............................................................................................................. 17 Digital meters ................................................................................................................................ 18 Calibration ..................................................................................................................................... 18 Frequency and time measurement ................................................................................................... 18 Resonance method........................................................................................................................ 19 Frequency – voltage conversion.................................................................................................... 19 Digital frequency meter................................................................................................................. 20 Digital time measurement ............................................................................................................. 21 Time interval measurement .......................................................................................................... 22 Phase shift measurement .............................................................................................................. 23 Generators......................................................................................................................................... 24 Generator basics............................................................................................................................ 24 Oscillator basics ............................................................................................................................. 24 amplitude condition phase shift condition of oscillation .......................................................... 24 Sound frequency oscillator ............................................................................................................ 24 Signal generators ........................................................................................................................... 25 Meissner oscillator .................................................................................................................... 26 Modulation ................................................................................................................................ 27 Function generators ..................................................................................................................... 29 Digital function generator ......................................................................................................... 30 Pulse - generator ........................................................................................................................... 30 Power supplies .................................................................................................................................. 32 AC – stabilized power supply......................................................................................................... 32 Swiching power supply .................................................................................................................. 34 Measurement and Instrumentation 2. Resistance measurement What is a resistance? 𝑈 ~ 𝐼, 𝑈 𝑅= , 𝐼 𝑙 𝑅 =𝜌∗ 𝐴 Using Ohms law (indirect measurement) Direct measurement (multimeters, two wires method) By comparison of measured voltages By comparison of measured currents Digital multimeter Electrical resistance is the easiest electrical property to measure precisely over a wide range at moderate cost. A simple digital multimeter costing a few tens of dollars can measure resistances in the range 10 ohm to 10 megaohm with a precision of about 1% using a two-wire technique (circuit 1). Circuit 1. Two-wire resistance measurement, RX = (V/I) − RL1 − RL2. The precision of the two-wire method is limited by uncertainties in the values of the lead resistances RL1 and RL2. Circuits 2 & 3. Three-wire resistance measurement methods. Providing the leads are well-matched, three-wire techniques can be used. Circuit 2 employs two matched current sources, I1 and I2, to eliminate the effects of lead resistance providing RL1 = RL2. Circuit 3 is an AC-bridge that is in-balance when RX = RY providing RL1 = RL3. If a lock-in amplifier is used as a null-detector, determination of RX with an extremely low excitation current is possible. The 4-Wire 'Kelvin' method (circuit 4) is used in difficult cases when lead resistances vary, RX is very small, or when very high accuracy is required. The method is immune to the influence of lead resistance and is limited by the quality of the constant current source and voltage measurement. Thermo-electric voltages can be eliminated by averaging two measurements with the polarity of the excitation current reversed. http://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects/project_ideas/Elec_p025.shtml Wheatstone bridge Impedance measurement What is the impedance? Rotating vectors My Sim 2 2 Current rotating vector Real current in time 1 Voltage rotating vector 0 -1 áramerősség, feszültség feszültség, áram y koordináta 1 0 -1 Real voltage in time -2 -2 -2 -1 0 feszültség, áram x koordináta 1 2 0 2 4 idő (sec) 6 8 Complex numbers – phasor reprezantation 𝑍̅ = 𝑍 ∗ (cos(𝜑) + 𝑖 ∗ sin(𝜑)) ̅ = 𝑍̅ ∗ 𝐼 ̅ 𝑈 𝑍̅ = 𝑍 ∗ (cos(𝜑) + 𝑖 ∗ sin(𝜑)) 𝑈𝑚𝑎𝑥 = 𝐼𝑚𝑎𝑥 ∗ 𝑍, 𝜑𝑈 = 𝜑𝐼 + 𝜑 Three voltmeters method Bridge methods - Balanced Bridge Maxwell – Wien Bridge Wien – Bridge Resonance method Digital multimeters Alternative images qualitiy factor loss factor Alternative image for real resistor Measuring impedances with vector voltmeter Power measurement DC – power measurement AC – power basics Active, reactive power, power factor, instantaneous power Three voltmeters measurement Wattmeters Electronic methods Digital methods Hall-sensor Energy measurement DC – meter Electrodynamic DC - meter Dc electric engine, without metal Aluminium disc with permanent magnet Using by electromagnetic induction Magnetic field Torque Turning plate Counter Ac induction energy meter Electronic energy meters Analog multipliers Digital meters Calibration Frequency and time measurement Frequency and Periodic Time measurement T (sec) Resonance method Measuring frequency Resonance method: -mechanical -AC RLC circuits measured current C1 1u R1 1k f0 1 2 L C L1 1m AM1 + + R2 1k A VG1 Resonance at f_0 frequency frequency Frequency – voltage conversion Frequency conversion method Effective U of the pulse signal proportional to frequency of the sinus signal Digital frequency meter Digital time measurement Time interval measurement Phase shift measurement Generators Generator basics Oscillator basics amplitude condition phase shift condition of oscillation Sound frequency oscillator Signal generators Meissner oscillator Modulation Function generators Digital function generator Pulse - generator Power supplies AC – stabilized power supply Swiching power supply