* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is sound?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
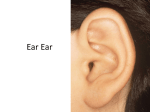
Chapter 42: Sound What you need to know • • • • • • • What is sound? How is it produced? How does it travel? How quickly does it travel? What are echoes? How does the ear work? How do we measure noise? What is sound? Sound is a form of energy which is caused by vibrations e.g vocal chords vibrate – voice strings vibrate - guitar. Sound is a form of Kinetic Energy Transmission of Sound Sound needs a material to pass through In space there is no sound………………because there is no medium – Astronauts need to communicate with each other using radios. Sound moves more quickly through solids than liquids and more quickly through liquids than gases How it works Sound is carried through the air by vibrations of air particles. If you speak into a loudspeaker it vibrates the air particles near you. The air particles beside them vibrate also. These vibrations travel through the air until they reach your ear and cause your eardrum to vibrate. If there was no air (i.e. medium) the vibrations could not travel How quickly does sound travel? • Light travels faster than sound • We know this because we see lightening before we hear thunder Speed of Sound Sound travels very fast It travels at 340 m/second Over long distances there is a lag time e.g. from seeing the light to hearing the sound e.g. fireworks. Experiment to Show that Sound Cannot Travel through a Vacuum What are echoes Echoes are sounds that are reflected from a surface Echoes Advantages of Echoes: Ships uses echo sounding to find the depth of the sea. Disadvantages of Echoes: Reflected sound can get mixed up with new sound and arrive together to the audience in a theatre. Example 2 • Sound is sent down to the seabed by a ship. A receiver on the ship picks up its echo 1.2 seconds later. If the speed of sound in water is 1500m/s calculate the depth of the water beneath the ship. Distance = speed x time Distance travelled by sound = 1500 x 1.2 = 1800m But depth of water is half distance travelled by water (ie up and down) 1800 /2 = 900m Example Suddenly a shoal of fish swims under the ship at a depth of 250m below the surface. How long does it take for the receiver to pick up the signal now? This time the sound travels 250m down and 250m back a total distance of 500m Time = distance / speed = 500 / 1500 = 0.33 seconds. Sound Detection in the Ear The outer ear is shaped to collect sound. The eardrum is like a thin drum skin and it vibrates when sound hits it. The vibration is carried through your middle ear into your inner ear. Nerves pick up the vibration and send electrical signals to your brain Our Ear Our Ears Our ears are extremely sensitive to sound. A sound level meter is used to measure sound. The decibel scale is used to measure sound. Sounds above 85 decibels can be harmful to your ears. Decibels • On the decibel scale, the smallest audible sound (near total silence) is 0 dB • * A whisper - 15 dB • * Normal conversation - 60 dB • * A car horn - 110 dB • * A rock concert or a jet engine - 120 dB • * A gunshot or firecracker - 140 dB • Any sound above 85 dB can cause hearing loss, and the loss is related both to the power of the sound as well as the length of exposure. You know that you are listening to an 85-dB sound if you have to raise your voice to be heard by somebody else. Eight hours of 90-dB sound can cause damage to your ears; any exposure to 140-dB sound causes immediate damage (and causes actual pain) Decibel Scale Noise Level & Damage Sounds about 85 Decibels (dB) can be harmful to your ears. The threshold of pain is about 130dB Hearing Protection 1. Obey warning signs. 2. Wear ear muffs. 3. Move away from the source of the sound. 4. A high wall or trees will reduce the noise from a busy road. Summary of Chapter