* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sequential Circuit Design
Survey
Document related concepts
Multidimensional empirical mode decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Curry–Howard correspondence wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
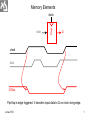
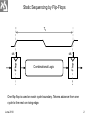
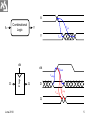
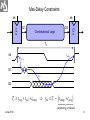
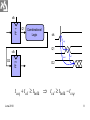
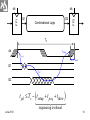
Memory Elements data Flop clock Q clock data Q-flop Flip-flop is edge triggered. It transfers input data to Q on clock rising edge. June 2010 1 Static Sequencing by Flip-Flops TC Combinational Logic Flop clk Flop clk One flip-flop is used on each cycle boundary. Tokens advance from one cycle to the next on rising edge. June 2010 2 Sequencing Elements Timing Notations t pd Logic Propagation Delay tcd Logic Contamination Delay t pcq Flop Clock-to-Q Propagation Delay tccq Flop Clock-to-Q Contamination Delay June 2010 3 t pdq Flop D-to-Q Propagation Delay tcdq Flop D-to-Q Contamination Dela tsetup Flop Setup Time thold Flop Hold Time June 2010 4 A Combinational Logic A t pd Y tcd Y clk clk thold D Flop tsetup Q D tccq t pcq Q June 2010 5 Max-Delay Constraints Q1 D2 Combinational Logic FF2 clk FF1 clk TC clk tsetup t pcq Q1 t pd D2 Tc t pcq t pd tsetup t pd Tc tsetup t pcq sequencing overhead June 2010 6 Min-Delay Constraints Logic circuits cannot be too fast. Otherwise the input data to next sequential circuit will change while it is still holding its current data. Such malfunction is called race condition, hold time failure or min-delay failure. FF1 clk Q1 Combinational Logic clk tccq Q1 clk D2 FF2 thold tcd D2 tccq tcd thold tcd thold tccq June 2010 8 Clock Skew • Clock should theoretically arrive simultaneously to all sequential circuits. • Practically it arrives in different times. The differences are called clock skews. • Clock skew consists of the following components: – Systematic is the portion existing under nominal conditions. It can be minimized by appropriate design. – Random is caused by process variations like devices’ channel length, oxide thickness, threshold voltage, wire thickness, width and space. It can be measured on silicon and adjusted by delay components. July 2010 9 Q1 D2 Combinational Logic FF2 clk FF1 clk TC clk tsetup t pcq tskew Q1 t pd D2 t pd Tc tsetup t pcq tskew June 2010 sequencing overhead 10