* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Perimeter lesson plan
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
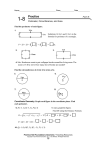
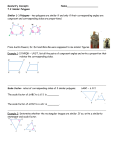
D. Bean Foundations of Mathematics Lesson Plan Name: Daneika Bean Course: Foundations of Mathematics Department: Mathematics Year Level: S1 Week: 1 Timeline: Two 50 minute lessons Materials: Key Terms: Geometry Measurement Perimeter Units Sum Plane Figures/Polygon (regular and irregular) Congruent Mathematics Connections Textbook Calculator String Ruler Writing tools (3minimum) D. Bean Foundations of Mathematics Lesson Plan INITIAL TEACHING Lesson Objectives: All Students Will Be Able To (A.S.W.B.A.T): Determine the perimeter of various regular and irregular plane figures. Students will also be able to apply the concepts of perimeter to solve problems. Do Now Activity: Take out at least 3 writing tools. Connect them together to make a closed figure and determine the PERIMETER the best way you know how. A ruler and string is provided for your use. Motivate and Activate: Discuss the various methods students used to determine the perimeter of their polygon. Since many students may make triangles or quadrilaterals, this is an opportunity to briefly touch on the different types of polygons, in particular the various types of triangles (equilateral, isosceles, scalene) and quadrilaterals (square, rectangle, rhombus, trapezoid, parallelogram) depending on if they used pens/pencils of the same length. Instructional strategies: Brainstorming, Hands-On Applications, Illustrations and Cooperative Learning. PRACTICE Guided Practice Activities: Review the key terms: PERIMETER – The distance AROUND any polygon. It is determined by calculating the SUM of all sides. SUM – the answer from adding numbers. PLANE FIGURE / POLYGON – a closed, flat, 2-dimensional shape(from Triangle to Decagon) REGULAR FIGURE – the sides and/or angles are congruent IRREGULAR FIGURE – the sides and/or angles are NOT congruent CONGRUENT - the sides and/or angles are the SAME / EQUAL. If P = 20cm and the width of this rectangle is 2cm, what is the measurement of the missing sides? 20cm – (2cm +2cm) = 16cm remaining Therefore 16 ÷ 2 = 8cm The sides of the rectangle are width 2cm; and length 8cm If P = 42in for a hexagon with all congruent sides, what is the measurement of each side? 42 ÷ 6 = 7cm The measurement of each side is 7cm Independent Practice Activities: Perimeter Practice Worksheet 2-8 Homework: Word Problems from Mathematics Connections Textbook, #’s 13 – 21 p.59 FORMATIVE ASSESSMENTS Students will be assessed on their ability to: 1) Collaboratively use educated reasoning skill to determine how to use other tools to determine Perimeter of various shapes 2) Progressively move towards completing a comprehensive written assignment on Perimeter and Circumference Enrichments: Correctives: Problems solving questions: Ex. Draw and label as many Isosceles Triangles as possible that have a perimeter of 10cm. String is used to show students that perimeter is the distance AROUND a figure. Therefore the base of a triangle for the roof of a house would not be included when determining the perimeter of the house. Closure: Review Key Terms and then use them to introduce the similar concept of Circumference of Circles.