* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Role of GIS in the Transport Sector
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
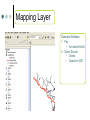
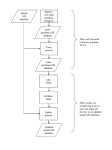
Role of GIS in the Transport Sector BBL, Jannuary 24th, 2005 Why GIS? Transport Managers/Administrators face a number of challenges Allocating Capital Investment Budgets. Managing and Maintenance of Existing Network Infrastructure. Negotiating with/ Educating decision makers. GIS Can Help!!! Outline Capital Investments Example: 1. Railroad branch closure 2. Essential road network Maintenance Examples: 1. Building a bridge maintenance system Educating Decision Makers Examples: 1. Put in a description of chems example here What is GIS? 1. Components of a GIS system 2. Technical Expertise 3. Costs Railroad Branch Closure Impact on People Impact on Industry Essential Road Network Minimum overall road network size to connect all towns. Minimizing maintenance costs Minimizing travel distance between towns Components of GIS System Interface Layer Database Layer Mapping Layer Manages the Data: The core of system: •Shape of a road • Maps the selected queries •Size of a bridge etc •Population data •Etc… •Processes the data •Define queries for the database layer •Create Interfaces for the user Database Layer Example Software: 1. Pay • Oracle • Microsoft SQL • Arcview/ArcInfo 2. Open Source • MySQL • Postgres SQL • Firebird Mapping Layer Example Software: 1. Pay • Arcview/ArcInfo 2. Open Source • Grass • Quantum GIS Application Layer Presents non technical users with a simple interface to display and edit data in the database and mapping layers. 1. Benefits • Easy to use • Accessible to a large number of user (e.g. through a web interface) • Control, data can only be viewed and modified in certain ways. 2. Limitations • Data can only be viewed and modified in predetermined ways. • Small overhead in developing the user interface. Example Software to develop applications: 1. Pay • ArcIMS • ArcScript • ASP 2. Open Source • MapServer • PHP • Perl Example applications: • Mapquest • Store Locators • … Technical Capacity Interface Layer Database Layer Mapping Layer To use To Implement No technical expertise required. Simple training with a specific application. Expertise required in GIS concept, database maintenance, GIS software packages and other middleware. Expertise required in GIS concepts and database maintenance. Expertise required in GIS concepts and database maintenance. Expertise required in GIS concepts and specific GIS software package. Expertise required in GIS concepts and specific GIS software package. Bridge Maintenance Anatomy of an open source GIS System Database Layer 1. Application: • Postgres SQL 2. Functions: • Stores all the data about the bridges and the underlying road network, as well as maintenance schedules and inspection reports 3. Cost Implications: • Free Software • Reusable Design Application Layer 1. Application: • Grass 2. Functions: • Draw all the maps and link objects on the map to the underlying database. 3. Cost Implications: • Free Software • Reusable Design Interface Layer 1. Application: • Mapserver • PHP • Apache 2. Functions: • Present the user with the forms and maps necessary to use the application 3. Cost Implications: • Free Software • Reusable Design A cost effective, GIS system? Use open source software 1. Software is free Exploit scale since there are no licensing fee Only let users interact at the Interface Level 2. Reduce technical expertise requirements from client countries. (development work can be done by the bank) Maximize reusability benefits. (a given application can easily be replicated to numerous countries) Use a Client-Server Architecture (Web Based) 3. Ensure maximum penetration (Simple web based interface ensures that low powered computers and multiple users can use the system). Server resources are pooled to exploit economies of scale