* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 164 study guide digestion
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
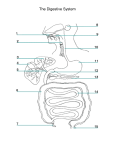
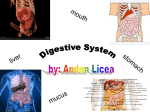
Biology 164 – Study Guide Digestive System Chapter 15 Terms Be familiar with the definition and physiological/anatomical significance of: bile, brush border, brush border enzymes, chyme, chief cells, cholesterol, defecation reflex, emulsification, gallbladder, gastric juice, haustra, heterocrine gland, lipases, microvilli, mucosa, muscularis externa, pancreatic amylase, parietal cells, pepsinogen/pepsin, peristalsis, plica circulares (intestinal folds), salivary α-amylase, salivary glands (parotid, submandibular, sublingual), serosa, submucosa, submucosal plexus, villus (villi) To what extent do plica circulares (intestinal folds), villi, microvilli each increase the internal surface area of the small intestinal? How much greater is the internal surface area of the small intestine than it would be without all of these modifications? Why is this important? What are five general functions of the digestive system? Know the general plan for the layers of digestive tract. I.e. mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, serosa/adventitia. What is found in each of these layers? E.g. mucosa = epithelium, lamina propria, muscularis mucosae. Know the major function(s) of each organ of the digestive system that we discussed in class? Focus on how the structure of the layers of a particular portion of the digestive tract is related to its specific function. E.g. The stomach has three (3), not two (2), layers of smooth muscle in its muscularis externa → a major function of the stomach is mechanical digestion. E.g. Brunner’s glands in the duodenum protect it from acidic chyme from the stomach. What is the individual functions of the amylase, buffers and mucus found in saliva? What cell types are found in the mucosa of the stomach? Functions of these? Be familiar with the many general functions of the liver. Be familiar with Table 15.1, Review of Structures of the Gastrointestinal Tract and Table 15.3, Review of Accessory Structures of the Digestive System. Why is bicarbonate present in pancreatic juice? What is meant by the term “intestinal brush border”? How is the brush border important to digestion? What role do bile salts play in lipid digestion? Which organ is responsible for most of the digestion that occurs in the digestive tract? Which organ reabsorbs the most water? Practice questions 1. The layer of the gastrointestinal tract that is actually in contact with ingested food is the ___. a. adventitia b. mucosa c. muscularis externa d. serosa e. submucosa 2. One of the salivary glands releases a watery fluid containing salivary amylase and almost no mucus into ducts that open into the mouth near the upper second molar. This is the ___ salivary gland. a. parotid b. sublingual c. submandibular d. submaxillary 3. Parietal cells secrete ___. a. alkaline (basic) mucus d. hydrochloric acid 4. a. b. c. d. e. b. alpha-amylase e. pepsinogen c. gastric lipase Which of the following is NOT a function of the liver? activates Vitamin D detoxifies drugs interconverts organic molecules phagocytizes worn-out red blood cells secretes pepsin 5. The modification of the wall of the small intestine that increases its internal surface area to the greatest degree is the: a. cilia b. intestinal glands c. microvilli d. plica circulares (intestinal folds) e. villi 6. a. b. c. d. e. Which order is anatomically correct? stomach → duodenum → ileum → jejunum cecum stomach → duodenum → jejunum → ileum → cecum stomach → ileum → duodenum → jejunum → cecum stomach → ileum → jejunum → duodenum → cecum stomach → jejunum → duodenum → ileum → cecum 7. a. b. c. d. e. Which of the following is NOT true of the large intestine? it absorbs water it absorbs vitamins produced by bacteria its glands secrete digestive enzymes its goblet cells produce protective mucus its submucosa contains aggregations of white blood cells 8. Bile salts are enzymes that digest fats into fatty acids and monoglycerides. a. true b. false 9. The pancreas secretes bicarbonate ions into the ___ in order to ___ the pH of the chyme. a. duodenum; lower b. duodenum; raise c. stomach; lower d. stomach; raise 10. Bile is stored and is concentrated in the ___: a. gallbladder b. liver c. pancreas 1 2 3 4 B A D E 5 6 7 8 C B C B 9 B 10 A d. small intestine e. spleen