* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 9-Opener-CRT - MrD-Home
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
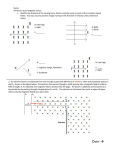
The Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) How it works…. • Electrons are boiled off in the cathode (negative terminal) • Electrons are sped up through accelerating plates (parallel plates with a potential difference) • Electrons are deflected by a second (and third) set of deflecting plates • Electrons hit a fluorescent screen to produce a picture The BIG Idea… Electric potential (Voltage) is "energy per charge" so ΔV = ΔEp/q ΔEp = qΔV is the kinetic energy given to charge q as it passes between the plates. This energy will accelerate the electrons! Other sets of parallel plates deflect the electrons up and down due to the electric field (and force) Common things to find…. • The transfer of potential to kinetic energy (and final velocity) from the accelerating plates • The electric potential (voltage) between the deflecting plates • The deflecting force (including direction) cause by the electric field between the plates • The final velocity of electrons when they leave the deflecting plates Check out this CRT applet An electron passing between parallel plates 0. 025 m apart experiences an upward electrostatic force of 5.1 x10-16 N. a) What is the magnitude of the electric field between the plates? b) What is the potential difference between the plates? c) On the diagram below draw in the connections to the power supply necessary for the electron to experience this upward force. 4 Chapters in 1 Question Vaccelerating = 900 V Vdeflection = 35 V Width of deflecting plates: 0.60 cm Length of deflecting plates: 2.5 cm a) Draw a sketch of the CRT b) Find the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the electron as it leaves the deflecting plates. Solution ΔEp = qΔV = (1.6x10-19)(900) = ½ mevx2 vx = 1.778*107 m/s Time between the deflection plates: t = d/v = 1.406*10-9 s Electric field in deflecting plates: E=V/d= 35/0.006 = 5.8*103 N/C or V/m Deflection force: F = qE = 9.33*10-16 N Upward acceleration: a=F/m = 1.02*1015 m/s2 Vy = 0 + at = 1.44*106 m/s Resultant velocity: 1.78*107 m/s Angle: tan-1(vy/vx) = 4.63o More Reading… Popular Mechanics Wikipedia-CRT