* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Origin and Structure of the Earth
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Van Allen radiation belt wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
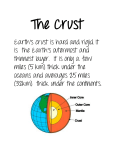
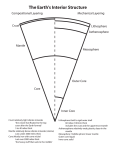
November 2012 System Closed any part of the universe that can be isolated for the purpose of observing and measuring change a system that does not allow matter to pass through its boundaries, but may allow energy to pass through its boundaries Open a system that allows both matter and energy to pass through its boundaries seismic waves (caused by earthquakes or giant man-made explosions) As waves pass through the Earth. They encounter different materials and change in important ways, becoming longer, shorter, faster, or slower. Magnetic field solid inner core made of iron (about 800 miles thick), liquid outer core (1370 mile thick) composed of iron-nickel alloy, oxygen. Magnetic Field: From the liquid outer core: seethes and roils like water in a pan on a hot stove. extremely hot and high pressure solid rock (iron-magnesium silicate, oxides) that accounts for about 80% of Earth’s volume, about 1750 miles thick. outermost compositional layer of the solid Earth, made of oxygen, silicon, and aluminum, 0-22 miles thick 1.Continental: thick, older, and buoyant, rocks like granite 2. Oceanic: thin, younger, and dense, rocks like basalt