* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nutrients and Their Functions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
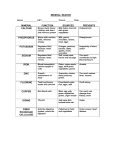
NUTRIENTS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS VITAMINS Vitamins are substances obtained from plant and animal foods that help regulate body functions. Vitamins do not provide energy (calories). They are essential for a variety of vital body functions. Each vitamin has a special job. NUTRIENT Vitamin A Vitamin D Vitamin E Vitamin K Thiamin (B I) Riboflavin (B2) Niacin FUNCTIONS IN BODY • Helps maintain healthy and smooth skin FOOD SOURCES Dark green leafy or yellow-orangered vegetables (spinach, broccoli, carrots, squash and sweet potatoes); some fruits (apricots, cantaloupe, • Improves resistance to infection mango and papaya). It is in dim light present in fairly large amounts in • Helps promote growth • Promotes health eyes and maintain liver. In the U.S., milk is fortified with Vitamin A. vision • Helps keep inner linings of mouth, ears, nose, lungs and digestive tract healthy • Promotes strong bones and teeth Eggs, liver and some fish; in the U.S. milk is fortified with Vitamin D. Exposure to sunlight allows the body • Aids in calcium absorption to make its own • Helps form red blood cells All vegetable oils like corn, cottonseed, olive and canola oils. Other sources include margarine and • Protects cell structure wheat germ. • Needed for normal blood clotting Dark green leafy vegetables, and members of the cabbage family; milk; soybean oil and egg yolks, cereals • Promotes proper nerve function, Present in many foods especially energy whole use grains, legumes (beans and peas), seeds, pork, and organ meats (liver, heart and kidney). In • Aids in digestion the U.S. most flours, cornmeal, rice, cereals and bakery products are • Promotes health appetite enriched and fortified with Thiamin. • Forms healthy skin, eyes Found in animal products (meat, poultry, fish, eggs and especially • Aids in release of energy (calories) dairy products). from food Other good sources include fortified cereals, enriched white flour and green vegetables (broccoli, asparagus, turnip greens, spinach) • Promotes appetite, digestion and Legumes (beans and peas), fish and nerve function organ meats, whole grains, peanuts, milk, dark green leafy vegetables. In • Aids in release of energy from the U.S. most flours and cereals are foods enriched with niacin. NUTRIENT Pyridoxine (B6) FUNCTIONS IN BODY • Aids in use of protein and carbohydrate • Helps form red blood cells FOOD SOURCES Wheat germ, whole grains, chicken, fish, pork, eggs and liver, legumes, fruits, nuts and vegetables especially avocados and bananas • Aids in nerve and brain function Pantothenic Acid • Needed to make hormones • Helps regulate nerve function Folic Acid (Polacin/Folate) • Essential for manufacture of red blood cells; prevents anemia Vitamin B12 (Cyanocobalamin) • Helps the body use protein • Essential for manufacture of red blood cells Biotin • Aids in proper functioning of nervous system • Aids in use of energy (calories) Vitamin C • Helps maintain skin, hair, and nervous system • Helps maintain healthy • Helps the body resist infection • Aids in healing of wounds, cuts, bruises and broken bones • Enhances absorption of iron Found in foods of both animal and vegetable origin. Good sources include whole grains, legumes, some vegetables and fruit, organ meats, yeast and egg yoke. Dark green vegetables and organ meats. Other good sources include legumes, oranges and whole grains Found only in meats, dairy products and eggs Best sources include egg yolk, liver, yeast and whole grains Primary sources are fresh fruits and Vegetables, especially citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruit), strawberries, green and red peppers, collard greens, broccoli, spinach, potatoes, papaya and mangos MINERALS Minerals are substances that perform a variety of vital functions in the body. Each mineral has a special job. Minerals do not provide energy (calories) NUTRIENT Calcium FUNCTIONS IN BODY • Build healthy bones and teeth FOOD SOURCES The best sources of calcium include all dairy products (milk, cheese, • Helps nerves and muscles function yogurt), dark green leafy vegetables (except spinach and chard), legumes properly (dried beans and peas), and the soft bones of canned fish (salmon and sardines) NUTRIENT FUNCTIONS IN BODY Copper • Needed to make red blood cells Fluoride • Helps with iron absorption • Helps build healthy bones and teeth Iodine • Helps to regulate thyroid function Iron • Aids in growth, reproduction, • muscle and nerve function • Needed for making hemoglobin in red blood cells; gives blood its red color, Hemoglobin carries oxygen to all cells in the body Manganese • Aids in normal growth • Needed for normal bone formation Magnesium • Promotes bone growth • Aids in energy use Phosphorus • Helps nerves and muscles work • Helps build bones and teeth Potassium • Helps regulate blood pressure Sodium • Essential for nerve and muscle function products and most meats. Good sources • Helps regulate blood pressure Zinc • Helps maintain body fluid balance • Involved in breakdown and utilization of carbohydrates and in protein synthesis • Necessary for normal growth and development • Important for health of many cells (e.g. taste buds, lining of gastrointestinal tract, immune system, retina of eye) • Important in transport of carbon dioxide FOOD SOURCES Seafood and shellfish, organ meats (liver, heart, kidney), whole grains, and nuts The richest dietary sources of fluoride are tea, fish, the soft bones of some fish (salmon and sardines), and fluoridated water Most seafood (shrimp, haddock, cod). In the U.S. salt is fortified with iodine (iodized salt) Meats, fish, seafood, poultry, eggs, organ meats (liver, kidney, heart), legumes (dried beans and peas); nuts and seeds, whole grains, dark molasses, green leafy vegetablesand fortified cereal products Whole grains and cereal products are the richest sources Whole grains, legumes (dried beans and peas); nuts, and green leafy vegetables Found in most foods. Good sources include meats, poultry, fish, milk and milk products, eggs, grains and legumes (dried beans and peas) Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, dairy Meat, poultry, milk, eggs, table salt, and seafood Most of the salt we eat comes from eating processed foods Whole grains, soy protein, meat, poultry (esp. dark meat), oysters, eggs and legumes (dried beans and peas). NUTRIENT Protein FUNCTIONS IN BODY • Makes new cells and tissues • Renews/repairs body cells and tissues FOOD SOURCES Meat, poultry, fish, legumes (dried beans and peas), nuts and seeds, eggs, dairy product • Forms antibodies to help fight infection Carbohydrates Fat • Supplies energy_(calories) • Supplies energy (calories); energy enables the body to do physical and mental work; maintain and regulate body temperature; and is necessary for basic body functions (activity of organs and cells) • Supplies energy (calories) • Helps form healthy skin • Helps with absorption of some vitamins All fruits and vegetables, breads and other grains and legumes All meats, dairy products (except skim), vegetable oils, nuts, seeds and small amounts in grains