* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PACING GUIDE FOR
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Recurrence relation wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
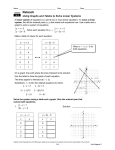
System of linear equations wikipedia , lookup
Partial differential equation wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
CONTENT *7.RP.1 Compute unit rates associated with ratios of fractions, including ratios of lengths, areas and other quantities measured in like or different units. For example, if a person walks ½ mile in each ¼ hour, compute the unit rate as the complex fraction 1/2/1/4 miles per hour, equivalently 2 miles per hour. TEXTBOOK Holt McDougal 4-1 p. 214 4-2 p. 218 7.RP.2 Recognize and represent proportional relationships between quantities. a. Decide whether two quantities are in a proportional relationship, e.g., by testing for equivalent ratios in a table or graphing on a coordinate plane and observing whether the graph is a straight line through the origin. b. Identify the constant of proportionality (unit rate) in tables, graphs, equations, diagrams, and verbal descriptions of proportional relationships. c. Represent proportional relationships by equations. For example, if total cost t is proportional to the number n of items purchased at a constant price p, the 8-4 p.405 LCS Pacing Guide Holt McDougal 4-3 p. 222 4-4 p. 226 5-8 p. 313 1-10 p. 52 SUPPLEMENTAL RESOURCES AIMS-Proportional Reasoning *Playing at Math p. 124 *Taylor Made p. 185 *Are you Ideal? P. 195 AIMS- Down to Earth *Shoot the AIMS –Machine Shop *Watt Power p. 166 AIMS-Through the Eyes of the Explorers *Pacing the Yard p. 20 Kagan Pre-Algebra Pgs. 226 - 228 AIMS – Through the Eyes of Explorers *Sizing up Shadows Pg. 53 AIMS – Soap Film Bubbles *Soap Cookbook Pg. 92 AIMS – Fun with Foods *Cafeteria Critique Pg. 73 Math Partnership: A Tale of 2 Tune Companies Kagan Pre-Algebra: Pgs. 229 – 232 Kagan Algebra: Pgs 211 – 214 Kagan Geometry: Pgs 250 – 253 Algebra Textbook: Page 1 DIGITAL RESOURCES Learn NC 1.01 7th Grade Pre-Algebra 2nd Nine Weeks KEY VOCABULARY Ratio Rate Unit Rate Proportion Gross Product Scale Drawing Percent Table Graphing Proportional Equivalent Ratio Constant of Proportionality Diagrams Percent Increase Percent Decrease Customary Unit Direct Variation 2014 - 2015 relationship between the total cost and the number of items can be expressed as t = pn. d. Explain what a point (x, y) on the graph of a proportional relationship means in terms of the situation, with special attention to the points (0, 0) and (1, r) where r is the unit rate. 7.RP.3 Use proportional relationships to solve multistep ratio and percent problems. Examples: simple interest, tax, markups and markdowns, gratuities and commissions, fees, percent increase and decrease, percent error 7.EE.2 Understand that rewriting an expression in different forms in a problem context can shed light on the problem and how the quantities in it are related. For example, a + 0.05a = 1.05a means that “increase by 5%” is the same as “multiply by 1.05.” 7.EE.3 Solve multi-step real-life and mathematical problems posed with positive and negative rational numbers in any form (whole numbers, fractions, and decimals), using tools strategically. Apply properties of operations to calculate with numbers in any form; convert between forms as appropriate; and assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation LCS Pacing Guide NC-2 6-2 p. 290 6-5 p. 306 6-6 p. 311 p. 315 Activity 6-7 p. 316 6-8 p. 320 6-9 p. 325 6-10 p. 330 7-7 p. 371 Math Partnership: *Purposeful Percents *Percent Shopping Kagan Pre-Algebra: Pgs 233-248 Study Island – Ratio; Proportions ClassScape Pg. E29E30 Simple Interest Tax Mark-ups Markdowns Gratuities Commissions Tips Fees Percent Increase Percent Decrease Percent Error www.mset.rst2.edu/ portfolios/s/smith_ms/ toolsdev/topic1.htm (multi-step equations) Convert Reasonableness Mental Math Old Glencoe Book 6-6 & 6-7 p. 358-366 Old Glencoe: Section 9-8 Pg. 462 Section 9-9 Pg. 467-473 Resources for Algebra *Lining up Dominoes B-86 Two Step Equations: 7-1 p. 344 7-2 p. 348 7-3 p. 353 7-4 p. 358 7-6 p. 367 8-5 p. 410 Inequalities: 7-5 p. 363 Pre-Algebra with Pizzazz Pg. 216-218 Pg. 221 Holt McDougal: Problem Solving Workbook *Lesson 2-5 Pg. 16 YouTube: Multi-step Equation Word Problems Math Partnership: *Sweet Algebra *Balance Act I & II Page 2 2014 - 2015 strategies. For example: If a woman making $25 an hour gets a 10% raise, she will make an additional 1/10 of her salary an hour, or $2.50, for a new salary of $27.50. If you want to place a towel bar 9 3/4 inches long in the center of a door that is 27 1/2 inches wide, you will need to place the bar about 9 inches from each edge; this estimate can be used as a check on the exact computation. 8.EE.5 Graph proportional relationships, interpreting the unit rate as the slope of the graph. Compare two different proportional relationships represented in different ways. For example, compare a distance-time graph to a distance-time equation to determine which of two moving objects has greater speed. Holt McDougal 6-2 p.340 6-3 p. 344 *Fruit Bowl I & II *Taco Twister *An Inequality Story 8-1 p. 388 8-2 p. 393 8-3 p. 399 Kagan Pre-Algebra: pgs. 250 – 261 Kagan Algebra1: Pgs. 222 – 283 Teaching CCMS with Hands-On Activities *It’s Proportional p. 169 NCDPI 8th Grade Lessons for Learning: *Perplexing Puzzles 8.EE.7 Solve linear equations in one variable. a).Give examples of linear equations in one variable with one solution, infinitely many solutions, or no solutions. Show which of these possibilities is the case by successively transforming the given equation into simpler forms, until an equivalent equation of the form x= a, a = a, or a = b results (where a and b are different numbers). b).Solve linear equations with rational number coefficients, including equations whose solutions require expanding expressions using the distributive LCS Pacing Guide Chapter 7 7-2 p. 348 Holt McDougal 12-2 p. 700 12-3 p. 704 Kagan Algebra 1: Pg 180 – 183 Function Domain Range Unit Rate Slope Proportional Relationship Linear Equations Distance-Time equation & Graph Solutions Slope – intercept Form X and Y intercepts Combine Like Terms Multi-Step Equations Variables on Both Sides Resources for Algebra: *Pg B-89 Algebra w/ Pizzazz: *Pgs. 28-33 Punchline Book A: *1.7 *1.8 *2.11 *3.14 *3.15 Page 3 2014 - 2015 property and collecting like terms. *3.16 *4.2 *4.3 Teaching CCMS with Hands-On Activities *Which Doesn’t Belong p. 177 7.G.1 Solve problems involving scale drawings of geometric figures, including computing actual lengths and areas from a scale drawing and reproducing a scale drawing at a different scale. LCS Pacing Guide 6-3 p. 295 11-4 p. 586 Holt McDougal 4-8 p. 248 4-9 p. 252 4-10 p. 256 Middle School Mathematician: *Pg 50 *Pg 79 Math Partnership: Look Alike Rectangle Kagan Pre-Algebra: Pgs 231-232 Kagan Algebra1: Page 215 Page 4 Scale Scale Drawing Model Scale Factor Dimensions Model 2014 - 2015