* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AXILLA2008-10-30 15:064.1 MB
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
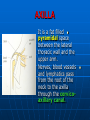
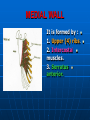
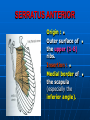
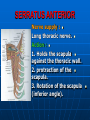
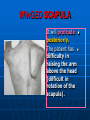
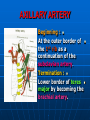
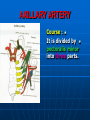
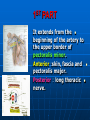
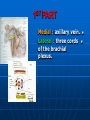
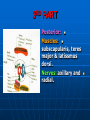
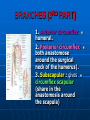
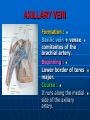
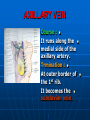
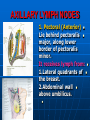
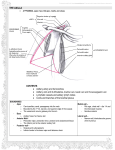
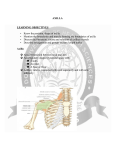
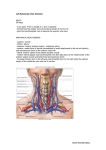
AXILLA It is a fat filled pyramidal space between the lateral thoracic wall and the upper arm. Nerves, blood vessels and lymphatics pass from the root of the neck to the axilla through the cervicoaxillary canal. BOUNDARIES The axilla has : 1. Apex : it is bounded by: In front : clavicle. Behind : upper border of the scapula. Medially : outer border of the first rib. BOUNDARIES 2. Base (lower end) It is formed by the hairy axillary skin. Its boundaries are: In front : anterior axillary fold. Behind : posterior axillary fold. Medially: chest wall. WALLS The axilla has the following walls : Anterior. Posterior. Medial. Lateral. The base is stretched between the anterior and posterior walls. ANTERIOR WALL Is formed by : 1. Pectoralis major. 2. Pectoralis minor. 3. Subclavius & Clavipectoral fascia. POSTERIOR WALL Formed by : 1. Subscapularis. 2. Latissmus dorsi. 3. Teres major. MEDIAL WALL It is formed by : 1. Upper (4) ribs. 2. Intercostal muscles. 3. Serratus anterior. SERRATUS ANTERIOR Origin : Outer surface of the upper (1-8) ribs. Insertion : Medial border of the scapula (especially the inferior angle). SERRATUS ANTERIOR Nerve supply : Long thoracic nerve. Action : 1. Holds the scapula against the thoracic wall. 2. protraction of the scapula. 3. Rotation of the scapula (inferior angle). WINGED SCAPULA Injury to the long thoracic nerve (in radical mastectomy) causes paralysis of serratus anterior. The medial border and inferior angle of the scapula will no longer be kept closely applied to the chest wall. WINGED SCAPULA It will protrude posteriorly. The patient has difficulty in raising the arm above the head (difficult in rotation of the scapula). LATERAL WALL It is narrow. It is formed by : 1. Bicipital groove of the humerus. 2. Biceps. 3. Coracobrachialis. CONTENTS 1. Axillary artery. 2. Axillary vein. 3. Cords of brachial plexus. 4. Axillary lymph nodes. 5. Fat. 6. Axillary sheath. AXILLARY ARTERY Beginning : At the outer border of the 1st rib as a continuation of the subclavian artery. Termination : Lower border of teres major by becoming the brachial artery. AXILLARY ARTERY Course : It is divided by pectoralis minor into three parts. RELATIONS The artery is enclosed throughout its course with the brachial plexus and the axillary vein with a sheath of deep fascia (Axillary sheath). 1ST PART It extends from the beginning of the artery to the upper border of pectoralis minor. Anterior :skin, fascia and pectoralis major. Posterior : long thoracic nerve. 1ST PART Medial : axillary vein. Lateral : three cords of the brachial plexus. 2ND PART It is behind pectoralis minor. Anterior : skin, fascia, pectoralis minor and major. Posterior : posterior cord of the brachial plexus, subscapularis. 2ND PART Medial : medial cord of the B.P. and axillary vein. Lateral :lateral cord of the B.P. 3RD PART It begins at the lower border of pectoralis minor and ends at the lower border of teres major by becoming the brachial artery. Anterior : pectoralis major, medial root of median nerve. 3RD PART Posterior: Muscles: subscapularis, teres major & latissmus dorsi. Nerves: axillary and radial. 3RD PART Lateral : Nerves musculocutaneo us. lateral root of median nerve. Muscles : biceps and coracobrachialis. 3RD PART Medial :Axillary vein. Nerves :ulnar and medial cutaneous nerve of the arm. BRANCHES First part : superior (highest) thoracic. Second part : A. Thoracoacromial. B. Lateral thoracic. BRANCHES (3RD PART) 1. Anterior circumflex humeral. 2. Posterior circumflex both anastomose around the surgical neck of the humerus). 3. Subscapular : gives circumflex scapular (share in the anastomosis around the scapula) AXILLARY VEIN Formation : Basilic vein + venae comitantes of the brachial artery. Beginning : Lower border of teres major. Course : It runs along the medial side of the axillary artery. AXILLARY VEIN Course : It runs along the medial side of the axillary artery. Trmination : At outer border of the 1st rib. It becomes the subclavian vein. AXILLARY LYMPH NODES They are (6) groups. They drain : 1. Lateral quadrants of the breast. 2. Thoracoabdominal walls above umbilicus. 3. Upper limb. AXILLARY LYMPH NODES 1. Pectoral (Anterior) Lie behind pectoralis major, along lower border of pectoralis minor. It receives lymph from: 1.Lateral quadrants of the breast. 2.Abdominal wall above umbilicus. AXILLARY LYMPH NODES 2. Subscapular (Posterior) Lie in front of subscapularis. Receives lymph of the back down to the iliac crest. 3. Lateral : Lie along medial side of the axillary vein. Receives from the upper limb except its lateral AXILLARY LYMPH NODES 4. Central : Lie in the axillary fat. Receives from the above three groups. 5.Infraclavicular (deltopectoral): Lie in the groove between pectoralis major and deltoid (outside axilla). AXILLARY LYMPH NODES 5.Infraclavicular (deltopectoral): Receives from lateral side of: Arm, forearm and hand. AXILLARY LYMPH NODES 6. Apical : Lie at the apex of the axilla , at the lateral border of the 1st rib. It receives efferent vessels from all the other lymph nodes. They drain into the Subclavian lymph trunk. DRAINAGE On right side : The trunk drains into right lymph trunk. On left side : It drains into thoracic duct.