* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Phylum Annelida - MR. Hill`s class
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
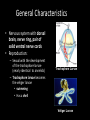
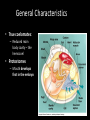
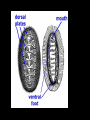
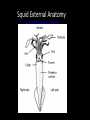
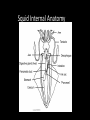
Phylum Mollusca • Soft-bodied Animals • More than 112,000 species General Characteristics • Bilateral Symmetry – Reduced segmentation • Three body parts – Head (contains mouth)muscular foot: • Locomotion, digging, supports internal organs • May be modified in squid and octopus – Visceral Hump (above the head) • Contains the internal organs (heart, organs of digestion, reproduction and excretion) – Mantle • Thin body covering (contains calcium carbonate) • Secretes shell • Reduce surface area for gas exchange evolved gills General Characteristics • Respiration – Gills(protected in mantle cavity), lungs, mantle or body surface • Nitrogenous wastes are excreted through nephridia • Open circulatory system with dorsal heart and vessels, hemocoel for return of circulatory fluid • Complete digestive system with mouth, radula= flexible tongue like strip of tissue covered with tough abarsive teeth that point backward – Radula is used to graze, drill, or function as a poisonous dart (or beak i.e. octopus) General Characteristics • Nervous system with dorsal brain, nerve ring, pair of solid ventral nerve cords • Reproduction: – Sexual with the development of the trochophore larvae (nearly identical to annelids) – Trochophore larvae becomes the veliger larvae • swimming • Has a shell Trochophore Larvae Veliger Larvae General Characteristics • True coelomates: – Reduced main body cavity – the hemocoel • Protostomes – Mouth develops first in the embryo Four classes • • • • Amphineura (polyplacophora) Bivalvia Gastropoda Cephalopoda Class Amphineura (Polyplacophora) – the chitons • Marine organisms • Shell is made up of 8 articulating plates • Have a muscular foot for locomotion (crawling) • Reduced head Chitons cont’d • About 650 species of these organisms • Cling to rocks in the intertidal zone and use a tooth-like radula to scrape food off of rocks (herbivores) • Breathe through gills Gumboot Chiton Class Gastropoda (Stomach-foot) • Largest molluscan class • Snails and Slugs, Sea slugs • Characterized by a single shell with characteristic cone shape • Breathe through gills (ctenidia) or the mantle cavity acts as a primitive lung (gas diffusion) • Muscular foot extends along the ventral surface of the organism Class Gastropoda • Gastropods undergo a process called torsion during larval development • The visceral mass twists 180 degrees in relation to the head • Results in the mantle cavity, gills and anus being brought to the front of the animal • Because of torsion the gastropod is able to retract its head into its mantle cavity when threatened Gastropods cont’d • Head contains a pair of antennae and a pair of eyes • Scraping radula to pick up food • Slug does not have a shell – Usually becomes active during the cool moist part of the day • Only molluscan class to become terrestrial • Open circulatory system – Circulatory fluid = hemolymph • Herbivorous or carnivorous Nudibranchs (Sea Slugs) • Marine gastropods that lack shells • Nudibranch means “naked gill” • refers to the fact that gas exchange happens across the entire surface of these animals Class Bivalvia (2 shells connected by hinge) • Clam, Oysters, Mussels, Scallops (most are sessile) • Mainly marine – living in intertidal zone • Large visceral hump and a muscular foot with a reduced head covered with a thin mantle • The mantle produces a cavity where the gills and 2 siphons (incurrent and excurrent) are found • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z BfviWg7kKM&feature=related Giant Clam Bivalvia cont’d • Filter feeders: – Take water containing food into the mantle cavity and pass it over the mouth – Excess water is forced out through the excurrent siphon • Oldest part of the shell is the area surrounding the hinge (called the umbo) • Exclusively marine • No radula Swimming Scallop • Burrow in sand or rock or attach to substrate by secreting byssal threads • Many leap with a foot • Separate sex – external fertilization Geoduck Mmmm oysters! Class Cephalopoda (Head-foot) • Squids, octopuses, cuttlefish, and nautilus • All members of this class are marine • Squid and octopus are among the most intelligent of the invertebrates • All carnivorous • Have tentacles and a central mouth containing a sharp beak Cephalopods cont’d • Many of these organisms contain a large ink sac that is used when trying to escape from potential predators • They have well developed eyes and brains • They contain special pigment cells called chromatophores which enable them to change color Squid Candles Cephalopods cont’d • They have gills in the mantle cavity • Their circulatory system is a closed one • Jet propulsion: Can force water out siphon • Catch prey with arms injecting poison with radula • Internal fertilization – lay eggs Squid External Anatomy http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e8RfE0mPsRc http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O5hEmZCuX0Y Squid Internal Anatomy