* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NAME: NWOSU CHIOMA GLORY LEVEL:100 COLLEGE: LAW
Survey
Document related concepts
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
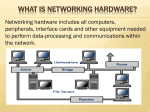
NAME: NWOSU CHIOMA GLORY LEVEL:100 COLLEGE: LAW COURSE: INTRODUCTION TO INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY COURSE CODE: GST 115 LECTURER: MR. ABIODUN OGUNTIMILEHIN QUESTION: DESCRIBE TEN EXAMPLES OF CONNECTIVITY HARDWARE Describe 10 examples of connectivity hardware The examples of connectivity hardware are explained below: HUBS: These are connective devices that come in all sizes and shapes and are available in a wide range of prices. They are “daisy chained “ together using short connection cables often referred to as a rat tail to the current hub. They do not contain any active electronics and make use of star topology. They are LANs (Local Area Networks) that provide greater port density. They are also known as reporters. They are of two categories which are: Active and Passive hubs. REPEATERS: They are electronic devices that receive signals and retransmit them. At a first glance, they look complicated but when taken apart piece by piece it becomes very easy to understand, it is not complicated. It is a ‘duplexed’ two-way radio set that listens on one frequency, and re-transmits what it hears on another frequency. They regenerate analog or digital signals distorted by transmission loss. BRIDGES: This is an interworking device that helps conserve the bandwidth available on the network. When LANs begin to grow, network data traffic can overwhelm the available bandwidth on network media by chopping the network up into smaller segments, which are connected to a bridge. Bridges are smaller than hubs and repeaters and use software as a help to do their job. They can read MAC addresses (hardware addresses) as well. They keep data traffic that is local to a particular segment from spreading to other network segments serviced by the bridge. SWITCHES: This is another interworking device that manages the bandwidth on a large network.they are rapidly becoming one of the most used connecting devices for connecting even smaller networks, because they allow control over the use of bandwidth on the network. They are also known as “bridge on steroids”, because they control the flow of data using the MAC address placed on each data packet. They divide data networks into Virtual Local Area Networks or VLANs ( a local grouping of computers on the network into a sort of communication group. The computers do not have to be close to each other and they combine software and hardware to switch packets between computers and other devices on the networks. ROUTERS: They have a very sophisticated Operating System (OS) that allows configuration of their various connection parts and are even smarter than bridges and switches. They segment LANs that have become very large and congested with data traffic. They also connect remote LANs together using different WAN technologies.they divide large networks into logical segments called subnets.they only forward data meant for other subnets on the extended networks to help conserve network bandwidth. They forward data packets based on a routing table, and use protocols built in to their Operating System to identify neighbouring routers and their network addresses such as IP addresses. GATEWAY: These are interface networks that use different protocols. Think of a gateway as a router that includes protocol translators. Gateways and routers are often used interchangeably but only gateways make it possible to connect networks using different protocols. However, any network that includes a mainframe system needs a gateway since this type of network uses different protocols. MODEMS: The term itself combines the first two letters of modulator and the first three letters of de-modulator which means it is a device used to modulate and demodulate data signals. It encodes digital computer signals into analog/analogue telephone signals and vice versa and also allows computers to communicate over a phone line. Modems can be used as a dial up for LAN or to connect to an ISP. It could be external as in the device which connects to a USB (Universal Serial Bus) or the serial port of computer or proprietary device for hand held gadgets and other devices as well as internal in the form of add-in expansion cards for computers . BROUTERS: Asi the name implies, it is a combination of bridges and routers. They take up both the functions of networking devices serving as a bridge when forwarding data between networks, and serving serving as a router when routing data to individual systems. They function as a filter that allows some data into the local network and re-direct unknown data to the other network. They are rare and their function is embedded into the routers routers functioned to act as bridges as well. NETWORK CARDS: it is known also Network Interface Cards (NICs) are hardware devices that connect a computer with the network. They are installed on the mother board, and are responsible for developing a physical connection between the network and the computer. Computer data is translated into electrical signals and sent to the network via NIC . NETWORK PROTOCOL: They define a language of instructions for communication between the network devices. It is essential for a networked computer to have one or more protocol drivers. For two or more computers to interconnect on a network, they must use identical protocols. At times, a computer is programmed to use multiple protocols. Network protocols like HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol), IP (Internet Provider) offer a basis on which much of the internet stands. REFERENCES. How to get started with modems, p.72 (1993) Telecommunications study.com Understanding Networking Hardware by Joe Habraken Nov. 7, 2003.