* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Al-Balqa` Applied University Faculty of Engineering Technology
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Light switch wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Dynamometer wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
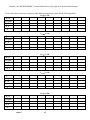
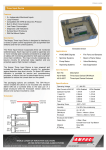
Al-Balqa' Applied University Faculty of Engineering Technology Mechatronics Engineering Department Electric Drive Laboratory Experiment Five Part II Investigation of three phase Squirrel Cage induction motor Variable Frequency Drive System Student’s Name: Supervisor: Date: DI-4000/AC Study Desk Experiment Objectives: 1- Studying and identifying the workbench components. 2- Investigation of three-phase squirrel cage motor electro-mechanical and torque-speed regulated characteristics by: A- Varying stator voltage and frequency (V/f= const). B- Varying frequency above nominal frequency with fixed stator voltage. Experiment Procedures: 1-Studying and identifying the workbench components A- Plot the experiment block-diagram or schematic diagram showing the main components Exp.5.II 1/5 B- Write down the specifications and parameters of each component - Main single-phase power supply: 230 V, 50 Hz. - Master switch “Main Switch”, magneto-thermal (16 A) and differential (0.03 A) protections. - Live desk warning lamp (‘Line”). - Low voltage main control complete with key selector (“ON”), emergency mushroom button with mechanical lock (“OFF”), warning lamp (“LINE 230 Vac”). - Reference potentiometer (“INTERNAL SPEED REFERENCE”). - Motor operation setting switch“DIN” . - RS 232 interface. - Two service plugs “SERVICE PLUG”; 230 V, 6 A, 50 Hz. - Safety bushings (2 mm and 4 mm) for signal check (“TP”). - Motor brake (“DC MOTOR BRAKE”, 1.5 kW) complete with thermo-switch (10 A) (“BRAKE POWER”) , warning lamp, thermal cut-off, bridge rectifier and variator: Power supply: three-phase, 230 V, 50 Hz Rated current, 6.77 A Output power , 1.5 kW Rotational speed, 1415 rpm - Three-phase squirrel cage ac motor: Power supply: Three-phase, 230 V/50 Hz Rated current, 4.9 A Output power, 1.1 kW. Rotational speed, 1415 rpm - Digital 4-digits ; frequency, stator voltage, stator current and dc link voltage meter. 2- Investigation of three-phase squirrel cage motor electro-mechanical and torque-speed regulated characteristics I- Preliminary steps (Experiment setup): - - Move the master switch (“MAIN SWITCH”) lever downwards. Move the (“BRAKE POWER”) switch lever downwards. Set all of the DIN 1, DIN 2, DIN 3, DIN 4, DIN 5 and DIN 6 switches to position “0”( i.e. lever downwards). DIN 1 set to the START/S TOP function. DIN 2 set to the REVERSE MOTOR function. DIN 3 set to the ALARM RESET function. DIN 4, DIN 5 and DIN 6 are not used. Turn the (“INTERNAL SPEED REFERENCE”) potentiometer knob fully to the left (zero reference). Set the (“INT/EXT”) switch lever to “INT” position, speed control by (“INTERNAL SPEED REFERENCE”) potentiometer. Turn the (“DC MOTOR BRAKE”) variator knob fully to the left (zero reference). Move the master switch (“MAIN SWITCH”) lever upwards, and then verify that the line lamp will come ON. Make sure that the emergency mushroom button (“OFF”) has been released. Turn the key selector (“ON”) to the right. Turn the (“INTERNAL SPEED REFERENCE”) potentiometer knob slowly to the right to set the desired speed level. Move the (“BRAKE POWER”) switch lever upwards. Exp.5.II 2/5 - Turn the (“DC MOTOR BRAKE”) variator knob slowly to the right to set the desired load torque. II- For each value of reference frequency under different load torque values fill the following tables: f ref 50 Hz TL , % n, rpm I1 , A V1 , V Vdc , V f ref 40 Hz TL , % n, rpm I1 , A V1 , V Vdc , V f ref 30 Hz TL , % n, rpm I1 , A V1 , V Vdc , V f ref 20 Hz TL , % n, rpm I1 , A V1 , V Vdc , V f ref 10 Hz TL , % n, rpm I1 , A V1 , V Vdc , V Exp.5.II 3/5 f ref 60 Hz TL , % n, rpm I1 , A V1 , V Vdc , V f ref 80 Hz TL , % n, rpm I1 , A V1 , V Vdc , V f ref 100 Hz TL , % n, rpm I1 , A V1 , V Vdc , V Exp.5.II 4/5 III- Plot regulated electro-mechanical characteristics related to natural characteristic and plot regulated torque- speed (mechanical) characteristics related to natural characteristic. IV- Results and Conclusions Exp.5.II 5/5