* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sedation For Medically
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
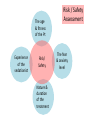
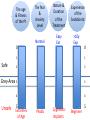
Sedation For Medically-Compromised Patients Is ASA Grading Out-dated? 2016 Dr Yusof (Joe) Omar MBBCh, DA, MRCA, PDD (Pain & Sedation) Sedationist Senior Teaching Fellow, Eastman CPD, UCL ASA I A normal healthy patient ASA II A patient with mild systemic disease ASA III A patient with severe systemic disease ASA IV A patient with severe systemic disease that is a constant threat to life Mrs X 66years old, retired, smoker, Alcohol 8-10u/w Lung disease, emhysema, usual Sats 87-89% Depression, under psychiatrist’s care. Steroids in the past Excessive thirst, pt thinks she may have Diabetes. Drugs: Inhalers only ASA I A normal healthy patient Healthy non-smoking, no or minimal alcohol use ASA II A patient with mild systemic disease Mild diseases only without substantive functional limitations. Examples include (but not limited to): current smoker, social alcohol drinker, (<14 u/w ) pregnancy, obesity (30 < BMI < 40), well-controlled DM/HTN, mild lung disease ASA III A patient with severe systemic disease Substantive functional limitations; One or more moderate to severe diseases. Examples include (but not limited to): poorly controlled DM or HTN, COPD, morbid obesity (BMI ≥40), active hepatitis, alcohol dependence or abuse, implanted pacemaker, moderate reduction of ejection fraction, ESRD undergoing regularly scheduled dialysis, premature infant PCA < 60 weeks, history (>3 months) of MI, CVA, TIA, or CAD/stents. ASA IV A patient with severe systemic disease that is a constant threat to life Examples include (but not limited to): Recent ( < 3 months) MI, CVA, TIA, or CAD/stents, ongoing cardiac ischemia or severe valve dysfunction, severe reduction of ejection fraction, sepsis, DIC, ARD or ESRD not undergoing regularly scheduled dialysis Mrs X 66years old, retired, smoker, Alcohol 8-10u/w Lung disease, emhysema, usual Sats 87-89% Depression, under psychiatrist’s care. Steroids in the past Excessive thirst, pt thinks she may have Diabetes. Drugs: Inhalers only Minor Surg Procedure. At Induction P 64/min BP 140/70 O2Sats 87% Midazolam 0.5 mg Total time 45min Total Midaz 1.5mg Total Propofol 20mg Uneventful Sedation Mrs X Escort took Mrs X back to Devon by car, no problems reported. How many of you would be happy with that? Mrs X was found dead the next morning. Did the Sedation contribute towards her Demise Post Mortem: No cause of death found. RETIRE NOW Is there an Alternative to ASA APACHE II Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II It is a severity-of-disease classification system (Knaus et al., 1985) A conceptual model for outcome after surgery. Gary Minto, and Bruce Biccard Contin Educ Anaesth Crit Care Pain 2013;bjaceaccp.mkt020 © The Author [2013]. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Journal of Anaesthesia. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: [email protected] Surgery Specific Estimates Of Risk (Cardiac Risk) High risk (cardiac risk >5%) Eg Open aortic Intermediate risk (1–5%) Eg Elective abdominal Low risk (cardiac risk <1%) Eg Dental (adapted from The Royal College of Surgeons of England/Department of Health3). © The Royal College of Surgeons of England. Taken from The Higher Risk Surgical Patient, 2011.3 Reproduced with permission. Risk Factors in Dental Sedation • • • • • • • • Age Fitness Fear and anxiety of Pt Nature of procedure Duration of procedure Training of sedationist Experience of sedationist Gut Feeling The age & fitness of the Pt Experience of the sedationist Risk/ Safety Nature & duration of the treatment Risk / Safety Assessment The fear & anxiety level The age & Fitness of the Pt The fear & Anxiety Level Nature & Duration of the Treatment Normal Easy Ext 0 Experience of the Sedationist >10y Exp 0 1 1 2 2 Grey-Area 3 3 4 4 5 Extremes of Age 5 Safe Unsafe Phobic Zygomatic Implants Beginner The age & fitness of the Pt Age: • -Within the experience & comfort zone of the sedationist Normal 0 ASA1 1 Safe 2 ASA2 Grey-Area ASA3 3 ASA4 4 Unsafe 5 Phobic • 16-59y treat as adults • 12-15 years: • 5-12 years: Individual assessment • 2-4 years: Is conscious sedation 0 3 35 really possible in a frightened child? 5 The age & fitness of the Pt ASA 1 0 1 Safe 2 Grey-Area 3 Fitness: RISK ASSESSMENT ASA 1= 0 ASA 4 = 5 L=Look externally (facial trauma, large incisors, beard or moustache, and large tongue) E=Evaluate the 3-3-2 rule (incisor distance <3 fingerbreadths, hyoid/mental distance <3 fingerbreadths, thyroid-to-mouth distance <2 1-5 fingerbreadths) M=Mallampati (Mallampati score ≥3 ) O=Obstruction (presence of any condition that could cause an obstructed airway) N=Neck mobility (limited neck mobility). 4 Unsafe 5 ASA 4 0 1 2 4 The fear & anxiety level 1 Phobics Difficult venipuncture They expect Oblivion Increased movements Increased Tremor Increased likelihood of vagal effects Undiagnosed problems Neglected OH Loose Teeth Normal 0 1 Safe 2 3 4 Unsafe 5 Phobic 4 5 Nature & duration of the treatment 0 Easy Ext 1 Safe 2 Grey-Area 3 4 Unsafe 5 Zygomatic Implants Lowest Risk: 1 Short, dry, procedure Anterior extractions Endo with Rubber dam Moderate Risk Duration of 2 hours or more 2 Two-Quad Restoration Scaling Sensitive Teeth without LA High risk Four Quad Surgery Complex Surgery Social reasons Public Transport Living alone 3 4 Experience of the Sedationist Training Formal Training PGCert or Grand-Father Skill in 0 Venipuncture Communication skills In simple CBT 1 Safe 2 Grey-Area 3 Experience Suggestions <20 cases/year = score 5 20-50 cases/y – score 4 50-100 cases/year = score 3 4 Unsafe 5 Up-to-Date: minimum ADA or SAAD annually Experience of the sedationist 0 1 Safe 2 Grey-Area 3 4 Unsafe 5 Training No Training Anaesth Training Skill 4 0 Venipuncture Communication skills In simple CBT Experience Suggestions <20 cases/year = score 5 20-50 cases/y – score 4 50-100 cases/year = score 3 Up-to-Date: minimum ADA or SAAD Score High Score and High Risk 6 0 Low Score and Safety A 4y old fallen off his Scooter, broken 2 teeth, and cut lip. Distraught mother, frightened child. Child wheezing but mum says it’s because he’s crying. Young dentist Sedates once /month Learnt to do it at Dental school and as SHO No PGC in Sedation 5 Total Score = 30 Age x 4y old Fitness x Asthma Fear Level x Crying 0 Nature of procedure Duration of procedure Training of sedationist Experience of sedationist 1 2 3 4 x ? Difficult x ? x Week-end Course x Low Gut Feeling: Under Pressure Mr MS aged 64y, BMI 33.5 •PMH Anaemia of unknown origin Asthma Knee probs Benign tumors of chest Diabetes Carpel tunnel release Heavy snorer MEDICATIONS : 1. Pravastatin 2. Dosulepin 3. Bumetanide 4. Meformin 5. Irbesartan 6. Tamsulosin 7. Novomix 8. Cocodomol 9. Amitriptyline 10. Ventolin 11. Omeprazol Mrs PP 95y old, mobile, lives independently PMH Angina, uses GTN very occasionally Pacemaker 2005 and 2014 Tripple CABG 2004 Hypertension L knee replacement 2010 Surgery to lower back 2014 Small cell Ca lunging remission Untreated Aortic Aneurism Cataracts Bunions Appendectomy MEDICATIONS : Aspirin Bendroflumethiazide 2.5mg Ramipril 1,25mg Isosorbide 10mg Bisoprolol 2.5 mg Lansoprazole Ferrous Sulphate Quinine Co-codomol Poswillo Report 1993-1995 no deaths Critical of the standard of care provided in: 1996-1999 eight deaths Of which five were children. • • • • Pre-operative assessment Monitoring Start of resuscitation and transfer to specialist critical care. General Anaesthesia, Sedation and Resuscitation in Dentistry, Report of an expert working party prepared for the Standing Dental Advisory Committee March 1990 (AKA The Poswillo Report). Thank you THE ULTIMATE IGNORANCE IS THE REJECTION OF SOMETHING YOU KNOW NOTHING ABOUT YET, REFUSE TO INVESTIGATE Dr Wayne Dyer