* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lab 2: Thévenin`s / Norton`s Theorem and Kirchhoff`s Laws
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
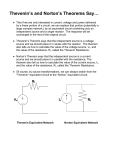
NORTHWESTERN UNIVERSITY Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE-221 Fundamentals of Circuits LAB 2: THÉVENIN'S / NORTON'S THEOREM AND KIRCHHOFF'S LAWS WORKSHEET 1: Theory 1 k 680 680 1 k 1.2 k 1.5 V 1.5 V 1.5 V 1.5 V 1 k 1.2 k (a) 150 (d) (c) (b) 560 Determine the Thévenin’s and Norton equivalents of each of the circuits in Fig. 1. Circuit (a): Voc = V Isc = Req = A A V Thevenin Circuit (b): Voc = Norton V Isc = Req = A V A Thevenin ECE 221 Lab 2 Worksheet Norton <Your Name> Page 1 Circuit (c): Voc = Isc = V Req = A V A Thevenin Circuit (d): Norton Voc = Isc = V A Req = V A Thevenin Norton 2: Thévenin's and Norton's Theorem 2.1 What defines an ideal voltmeter? An ideal ammeter? Answer 2.1 2.2 To find the internal resistance of the DAU when measuring currents, first set the DAU to measure current. Build the circuit in Fig. 2, and then use the oscilloscope to measure the voltage across the DAU connections. Finally divide this voltage by the measured current. Record V, I, and R = V/I below. Do you think this resistance will cause a significant error for our experiment? Answer 2.2 ECE 221 Lab 2 Worksheet <Your Name> Page 2 2.3. Fill in this table with the measured experiment (Vexp) and theoretical (Vth) voltages and the Iexp and Ith current for each circuit. Vexp Vth % error #DIV/0! #DIV/0! #DIV/0! #DIV/0! Iexp Ith %error #DIV/0! #DIV/0! #DIV/0! #DIV/0! Assessment and explanation of error: 2.4 What is an ideal voltage source? Answer 2.4 2.5 Fill in the table and plot (by hand) current vs. voltage. Draw a line extending to the current and voltage intercepts to graphically determine Voc (I = 0) and Isc (V =0). Resistance Voltage 2 3 4 5 7 9 40 110 Current V A Thévenin Norton 3: Kirchoff's Laws 3.1 DC (V) Vth Fxn Gen Power Supply R1 R2 ECE 221 Lab 2 Worksheet Vexp % error #DIV/0! #DIV/0! #DIV/0! #DIV/0! AC (V) Vth <Your Name> Vexp % error #DIV/0! #DIV/0! #DIV/0! #DIV/0! Page 3 Answer 3.1 3.2 Was the voltage across the power supply after connecting it to the circuit different from that which you set it initially? Can you explain the differences? Answer 3.2 3.3 I(Rl) = mA Sum of current at top node = I(R2) = mA I(R3) = mA I(pwr spl) = mA Answer 3.3 ECE 221 Lab 2 Worksheet <Your Name> Page 4 mA






![1. Higher Electricity Questions [pps 1MB]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000880994_1-e0ea32a764888f59c0d1abf8ef2ca31b-150x150.png)