* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2201_Homework_03
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Topology (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
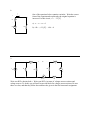
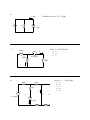
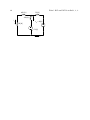
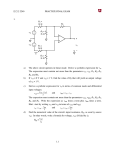
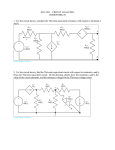
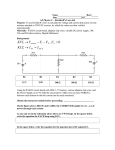
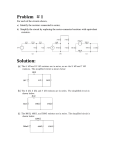
ECE 2201 – CIRCUIT ANALYSIS HOMEWORK #3 For each circuit there is a set of equations. Mark each equation as true or false. 1 + v1 - R1 + v2 vSA Figure 0.1 ______ a) vSA = v1 ______ b) vSA = v2 ______ c) vSA = v1 + v3 + R3 R2 v3 - - Figure 0.1 Figure 0.2 ______ d) vSA = v1 ______ e) v1 = v2 ______ f) vSA = vCSB ______ g) v1 = -v2 + + vCSB iSB R1 vSA v1 - - + R2 v2 - Figure 0.2 iVSA vSA R1 i1 i4 i2 R4 R2 R3 i3 Figure 0.3 . Figure 0.3 ______ h) iVSA = i1 ______ i) i3 = i4 ______ j) i2 = - i3 ______ k) i2 + i3 = iVSA 2 iC One of the equations below contains a mistake. Write the correct form of the equation and explain why the original equation is incorrect. For this circuit, vA = - 3.5 [V]. + + vB RB a) vC – vA – vB = 0 vC vA RC b) iCRC – (-3.5)[V] – iCRB = 0 - . 3 + R5 iS1 R1 vX - R4 R3 R2 vS2 vS1 R6 Write two KVLs that include vx. Write your KVLs in terms of voltages across resistors and voltage sources. To do this you will need to provide labels for voltages across resistors. Be sure these are clear, and that they follow the notation rules given in the first homework assignment. . 4 R4 vS1 R5 R1 vS3 R3 iS1 R2 For the circuit above: a) Label voltages for each resistor. b) Write three KVL equations using the voltages you defined. c) Label currents through each of the resistors. d) Rewrite your KVL equations, but this time for voltage across resistors use the product of current and resistance. Be sure to use the appropriate sign in each case. . 5 R4 vS3 vS1 R1 R5 R3 R2 iS1 For the circuit above: a) Label currents in each of the resistors. b) Write two KCL equations at any two essential nodes using the currents you defined. 6 Find the value of iS. R1 = 2.5[Ω]. ix = 1[A] R1 iS vx = 5[V] . 7 10[Ω] + vR Given: ix = 0.25[A], find: a. vX b. vR c. iS iS 10[Ω] + vS1=15[V] vX iX 25[Ω] - . 8 10[Ω] 5[Ω] + 5[Ω] + vR - + + vZ1 vZ2 - - iX vX vS1=-20[V] - i5 vS2=5[V] 5[Ω] 10[Ω] Given: i5 = - 1.5[A], find: a. vX b. vR c. iX d. vZ1 e. vZ2 9 + viS1 - vs1=120[V] A B For this circuit… iS1=0.15[A] 1[kΩ] 2.2[kΩ] iX 500[Ω] iY C D a. Write a KCL at A. b. Write a KVL around A•B•C•D c. Use your KCL and KVL to find ix, iy d. Find viS1. e. Find the power delivered to iS1. . . 10 vS1=-2.5(vX) Given: iZ = 1.1667[A], find: a. vX b. iY c. The power absorbed by vS1. + - 100[Ω] + iY 250[Ω] vX 50[Ω] vS2=-200[V] iZ Write 1 KCL and 2 KVLs to find i1, i2, i3. 11 105 [Ω ] 75 [Ω ] 250 [Ω ] i2 i1 45 [Ω ] vS2 = 40[V] vS1 = 72[V] i3