* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Total War
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Port Royal wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Cavalry in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fredericksburg wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Battle of White Oak Road wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Lexington wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Sailor's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Red River Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cumberland Church wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Malvern Hill wikipedia , lookup
Second Battle of Corinth wikipedia , lookup
List of American Civil War generals wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Harpers Ferry wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Appomattox Station wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Maryland Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
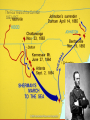
The Four Years of the Civil War 1861-1865 1861 Robert E. Lee rejects the North’s offer to be the General of the North. He could not fight against his home state. He becomes the head of the South/Confederates. Fort Sumter- the start of the war (South Carolina). The South fires on the Union troops protecting Ft. Sumter. Bull Run (Manassas), VA- 1861 Bull Run (Manassas) Showed the ability of Confederate leaders and tactics. (One of their greatest advantages). The Union was forced to retreat. The first major battle of the Civil War. Lesson learned: This war was going to last longer than 3 months. This was an eye-opening experience for the North. Generals: South- “Stonewall” Jackson, North- McDowell, McClellan Battles: 1862 1862- Antietam (Sharpsburg, Maryland) Antietam- bloodiest single day in America’s history (26,000 dead or wounded total) While technically a tie, the Union declared it a victory. Generals: South- Lee North- McClellan Union used this victory to issue the Emancipation Proclamation. ◦ Freed all slaves in the South (secession states only). ◦ Largely supported by abolitionists. ◦ This is an addition to the Northern reason for fighting the war. Not only for preservation of the Union, but know the war is about ending slavery too The Four Years of the Civil War 1861-1865 1863Chancellorsville, VA- Great victory for the Confederates (South). Stonewall Jackson accidentally shot by “friendly fire” and killed by his own men. His loss was a major blow to the South. Gettysburg, Pennsylvania1863 In terms of lives lost, more Americans lost their lives in this 3 day battle than any other. This battle marks the turning point of the Civil War. The South lost so many soldiers that Lee was forced to retreat and fight a defensive war for the remainder of the Civil War. Generals: Lee- South Meade- North Deadliest battle in American History. Pickett’s Charge- famous failed assault by the South at Gettysburg. This event will lead to the Gettysburg Address by Abe Lincoln. This event will lead to the Gettysburg Address. Gettysburg Address- Lincoln’s Most Famous Speech. What does it mean? Four score and seven years ago our fathers brought forth, upon this continent, a new nation, conceived in Liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal. Now we are engaged in a great civil war, testing whether that nation, or any nation so conceived, and so dedicated, can long endure. We are met here on a great battlefield of that war. We have come to dedicate a portion of it as a final resting place for those who here gave their lives that that nation might live. It is altogether fitting and proper that we should do this. But in a larger sense we can not dedicate - we can not consecrate - we can not hallow this ground. The brave men, living and dead, who struggled, here, have consecrated it far above our poor power to add or detract. The world will little note, nor long remember, what we say here, but can never forget what they did here. It is for us, the living, rather to be dedicated here to the unfinished work which they have, thus far, so nobly carried on. It is rather for us to be here dedicated to the great task remaining before us - that from these honored dead we take increased devotion to that cause for which they here gave the last full measure of devotion - that we here highly resolve that these dead shall not have died in vain; that this nation shall have a new birth of freedom; and that this government of the people, by the people, for the people, shall not perish from the earth. Gettysburg Address Main two points: 1. That the job is not yet done, and that the nation must be reunited to keep what we fought for in the Revolutionary War (Our freedom and Democratic system). 2. Pay respect to the dead from both sides in America’s most deadly battle. Vicksburg, Mississippi- 1863 Allowed the Union to take control of the Mississippi River and split the South in two. Remember this is one of the major ideas of the Anaconda Plan. Confederate soldiers dug deep into the sides of the hills for protections. Advanced military technology effectively trapped men in these caves. Generals: Grant- North Sherman’s March to the Sea 1864 March to the Sea (Atlanta)- William Sherman, of the North, uses “total war” to destroy Atlanta and most of the South. It devastates the Confederacy as Sherman uses the new form of warfare. The Four Years of the Civil War 1863-1865 Total War Total War- destroy everything in your path that can be used by the enemy. Goal: Make the South beg for the war to end. Destroy homes, factories, animals, crops, etc. End of the War- Appomattox Surrender at Appomattox, VA 1865 After experiencing months of total war- total destruction of all food, and supplies, Lee realized that the North’s blockade, destruction of the railroads and control of the Mississippi River would soon lead to mass starvation of Confederate of Confederate troops and citizens. Lee surrenders to Grant after the Burning of Atlanta and the battle of Appomattox. Although known as “ Unconditional Surrender,” Grant offered generous surrender terms.