* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Sun
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Advanced Composition Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
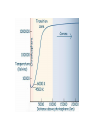
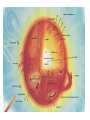
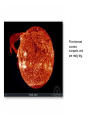
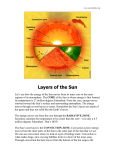
EARTH SUN (SOL) Radius = 1 Radius = 109 Density =1 Density = 0.255 Gravity =1 Gravity = 28.0 Temperature ~ 300K Temperature ~ 5,800K Photosphere Photosphere 1. Very thin 2. Emits Radiation 3. "Photo" means "light". This is the light sphere 1. Thin layer 2. Cooler than Photosphere 3. "Chromo" means "color". This is the color sphere Chromosphere Photosphere 1. Very thin 2. Emits Radiation 3. "Photo" means "light". This is the light sphere Transition zone 1. Starts getting warm in a hurry 2. Transitions from cool to hot, from Sun to Outer space. Chromosphere 1. Thin layer 2. Cooler than Photosphere 3. "Chromo" means "color". This is the color sphere Solar Wind, 2,000,000 K 0.000,000,000,000,000,000,000,02 g / m3 Corona, very hot and very low density 1,000,000 K .000,009 g / m3 Heat moves through convection (movement of material itself) 2,000,000 K NO fusion NO light given off Heat moves through convection (movement of material itself) 2,000,000 K NO fusion NO light given off Heat moves through Radiation (movement through radiation) 7,000,000 K NO fusion NO light given off Energy is created through fusion of hydrogen in to helium 15,000,000 K Getting hotter over time, started out at about 10,000,000 K Granulation is the tops of the convection Based on the total number of atoms, NOT mass. By MASS, 71% H, 27 % He One of those protons became a neutron, so in order to keep the Conservation of Energy happy, a positron is ejected from its nucleus. One of those protons became a neutron, so in order to keep the Conservation of Energy happy, a positron is ejected from its nucleus. This Helium only has one neutron. One of those protons became a neutron, so in order to keep the Conservation of Energy happy, a positron is ejected from its nucleus. This Helium only has one neutron. Left side has 6P and 2N Right side has 6P and 2N (& repeat) Sunspot is a cool place on the Sun. Convection is not working because of magnetism decay in that area. Heat not rising. Prominences connect sunspots, and are really big. Sunspot cycle is 11 years Solar Cycle is 22 years Solar flares are outward bursts. Coronal Mass Ejections are bigger than huge. One per day at solar minimum, two or three per day at solar True or False 1. The Sun is a rather normal star ________ 2.The Sun’s average density is less than that of Earth ________ 3.The Sun’s diameter is about 10 times that of Earth ________ 4.Sunspots show that the Sun’s poles spin faster than the equator ________ 5.Convection currents in the Sun involve cool gas rising toward the surface, and hot gas sinking to the interior ________ 6.The temperature of the solar atmosphere decreases with increasing altitude ________ 7.Prominences are large flames erupting from the burning surface of the Sun ________ 8.Positrons are the antiparticles of electrons ________ 9.Nuclei are held together by the strong force ________ Self-Test: Fill in the Blank 1.The part of the Sun that we see is called the ________ 2.Traveling outward from the surface of the Sun, the main regions of the solar atmosphere are the ________, the ________, and the ________. 3.Below the surface of the Sun, lie the ________ zone, the ________ zone and the ________ zone. 4.The most abundant element of the Sun is ________________ followed by ________________. 5.The two most abundant elements of the Sun make up about ________ percent of its composition (by number of atoms) 6.Sunspots appear dark because they are ________ than the surrounding gas of the photosphere. 7.The Sunspot cycle is ________ years long, but the solar cycle is ________ years long 8.The net result of the proton-proton chain is that ________ protons are fused into a nucleus of ________, two ________ are emitted, and energy is released in the form of ________________. Mass is ________.