* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ECE 3323 Section 2.1 Signals Power and Energy
Survey
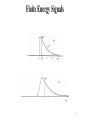
Document related concepts
Transcript
ECE 3323 Principles of Communication Systems Section 2.1 Signals Power and Energy 1 Definition of a Signal A Signal, denoted x(t), is assumed to be either a voltage or a current in an electrical system. Signals will be assumed to be Real Functions (as opposed to Complex, with real and imaginary parts) unless noted. 2 Signal Power A Signal is assumed to be measured across a 1 Ω resistance (in the case of a voltage) or measured through a 1 Ω resistance (in the case of a current) such that the instantaneous power of the signal is 𝑃= 𝑥 𝑡 2 Signals are assumed to be real valued, so the instantaneous power is 𝑃 = 𝑥2 𝑡 3 Finite Energy Signals The energy contained in a signal is the time integration of the instantaneous power. If this quantity is bound such that ∞ 𝐸= ∞ 𝑃 𝑑𝑡 = −∞ 𝑥 𝑡 2 𝑑𝑡 < ∞ −∞ the signal is known as an Energy Signal. This requires that the signal have non-negligible magnitude for only a finite amount of time. 4 Finite Power Signals If a signal exists for all time, the total energy in the signal may not be bounded. In these cases the average power in the signal is 𝑇 𝑃𝑎𝑣𝑒 1 = lim 𝑇→∞ 𝑇 2 𝑥 𝑡 2 𝑑𝑡 < ∞ −𝑇 2 𝑃𝑎𝑣𝑒 = 𝑥 𝑡 2 <∞ The signal is said to be a Power Signal. 5 Signal Classification Based on these two definitions, there are two classes of signals: 1. x(t) is an Energy Signal if and only if 0 < E < , implying that that P = 0. 2. x(t) is a Power Signal if and only if 0 < P < , implying that E = . 6 Finite Energy Signals 7 Finite Power Signals 8 Periodic Signals A signal is Periodic if and only if 𝑥 𝑡 + 𝑛𝑇0 = 𝑥 𝑡 for all t and integer n. The smallest positive number that satisfies this condition is the period T0. All other signals are Non – Periodic. 9 Periodic Signals 10 Deterministic Signals Signals whose values are defined for their entire existence are called Deterministic Signals. An explicit mathematical expression can be written for these signals. 11 Random Signals Signals whose values are not defined, or not predictable, are called Random Signals. A mathematical expression cannot be written. Random signals can be described by their statistical properties. 12 Continuous, Discrete, Analog or Digital? 13