* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 19-20 Review
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
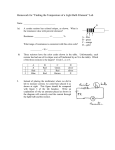
Chapter 19-20 Review Name:______________________ Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. How is current affected if the number of charge carriers decreases? a. The current increases. b. The current decreases. c. The current initially decreases and then is gradually restored. d. The current is not affected. ____ 2. The current in an electron beam in a cathode-ray tube is 7.0 x 10–5 A. How much charge hits the screen in 5.0 s? a. 2.8 x 103 C c. 3.5 x 10–4 C b. 5.6 x 10–23 C d. 5.3 x 10–4 C ____ 3. A wire carries a steady current of 0.1 A over a period of 20 s. What total charge moves through the wire in this time interval? a. 200 C c. 2 C b. 20 C d. 0.005 C ____ 4. When you flip a switch to turn on a light, the delay time before the light turns on is determined by a. the number of electron collisions per second in the wire. b. the drift speed of the electrons in the wire. c. the speed of the electric field moving in the wire. d. the resistance of the wire. ____ 5. When electrons move through a metal conductor, a. they move in a straight line through the conductor. b. they move in zigzag patterns because of repeated collisions with the vibrating metal atoms. c. the temperature of the conductor decreases. d. they move at the speed of light in a vacuum. ____ 6. The energy gained by electrons as they are accelerated by an electric field is a. greater than the average loss in energy due to collisions. b. equal to the average loss in energy due to collisions. c. less than the average loss in energy due to collisions. d. not affected by the gain in energy due to collisions. ____ 7. The drift velocity in a wire is a. the average speed of electrons between collisions. b. the energy gained by electrons as they are accelerated by an electric field. c. the speed at which an electric field reaches electrons throughout a conductor. d. the net velocity of a charge carrier moving in an electric field. ____ 8. In alternating current, the motion of the charges a. continuously changes in the forward and reverse directions. b. is equal to the speed of light. c. is greater than the speed of light. d. in the direction of the electric field. ____ 9. A light bulb has a resistance of 240 when operating at 120 V. What is the current in the light bulb? a. 2.0 A c. 0.50 A b. 1.0 A d. 0.20 A ____ 10. Which of the following wires would have the LEAST resistance? a. an aluminum wire 20 cm in diameter at 40oC b. an aluminum wire 20 cm in diameter at 60oC c. an aluminum wire 40 cm in diameter at 40oC d. an aluminum wire 40 cm in diameter at 60oC ____ 11. What happens to the resistance of a superconductor when its temperature drops below the critical temperature? a. The resistance is equal to that of a semiconductor with the same dimensions. b. The resistance doubles. c. The resistance drops to zero. d. The resistance reduces by one-half. ____ 12. When compared in a given time interval with other light bulbs in a 120 V outlet, a 60 W light bulb a. converts the same electrical energy to heat and light than a 40 W light bulb. b. converts more electrical energy to heat and light than a 100 W light bulb. c. converts less electrical energy to heat and light than a 40 W light bulb. d. converts less electrical energy to heat and light than a 100 W light bulb. ____ 13. Tripling the current in a circuit with constant resistance has the effect of changing the power by what factor? a. c. 3 b. d. 9 ____ 14. If a 325 W heater has a current of 6.0 A, what is the resistance of the heating element? a. 88 c. 9.0 b. 54 d. 11 ____ 15. If a lamp has a resistance of 120 when it operates at a power of 1.00 x 102 W, what is the potential difference across the lamp? a. 110 V c. 130 V b. 120 V d. 220 V ____ 16. If a lamp is measured to have a resistance of 45 when it operates at a power of 80 W, what is the current in the lamp? a. 2.10 A c. 0.91 A b. 1.3 A d. 0.83 A ____ 17. A high-voltage transmission line carries 1000 A at 700 000 V. What is the maximum power carried in the line? a. 700 MW c. 100 MW b. 400 MW d. 70 MW ____ 18. How much does it cost to operate a 695 W heater for exactly 30.0 min if electrical energy costs $0.060 per kWh? a. $0.02 c. $0.18 b. $0.90 d. $0.36 ____ 19. A microwave draws 5.0 A when it is connected to a 120 V outlet. If electrical energy costs $0.090/kWh, what is the cost of running the microwave for exactly 6 h? a. $2.70 c. $0.72 b. $1.60 d. $0.32 ____ 20. Which of the following does NOT affect a material’s resistance? a. length c. temperature b. the type of material d. Ohm's law ____ 21. If the potential difference across the bulb in a camping lantern is 9.0 V, what is the potential difference across the battery used to power it? a. 1.0 V c. 9.0 V b. 3.0 V d. 18 V ____ 22. If the batteries in a portable CD player provide a terminal voltage of 12 V, what is the potential difference across the entire player? a. 3.0 V c. 6.0 V b. 4.0 V d. 12 V ____ 23. How does the potential difference across the bulb in a flashlight compare with the terminal voltage of the batteries used to power the flashlight? a. The potential difference is greater than the terminal voltage. b. The potential difference is less than the terminal voltage. c. The potential difference is equal to the terminal voltage. d. It cannot be determined unless the internal resistance of the batteries is known. ____ 24. Three resistors with values of 4.0 , 6.0 , and 8.0 , respectively, are connected in series. What is their equivalent resistance? a. 18 c. 6.0 b. 8.0 d. 1.8 ____ 25. Three resistors connected in series have voltages labeled V1, V2, and V3. Which of the following expresses the total voltage taken over the three resistors together? a. Vt = V1 + V2 + V3 c. Vt = V1 = V2 = V3 b. Vt = (1/V1 + 1/V2 + 1/V3) d. Vt = (1/V1 + 1/V2 + 1/V3)–1 ____ 26. Three resistors with values of 4.0 , 6.0 , and 10.0 are connected in parallel. What is their equivalent resistance? a. 20.0 c. 6.0 b. 7.3 d. 1.9 ____ 27. Three resistors connected in parallel carry currents labeled I1, I2, and I3. Which of the following expresses the total current It in the combined system? a. It = I1 + I2 + I3 c. It = I1 = I2 = I3 b. It = (1I1 + 1/I2 + 1/I3) d. It = (1I1 + 1/I2 + 1/I3)–1 ____ 28. Two resistors with values of 6.0 and 12 are connected in parallel. This combination is connected in series with a 4.0 resistor. What is the overall resistance of this combination? a. 0.50 c. 8.0 b. 2.0 d. 22 ____ 29. What is the equivalent resistance for the resistors in the figure above? a. 2.3 c. 13 b. 5.2 d. 22 ____ 30. What is the equivalent resistance for the resistors in the figure above? a. 25 c. 7.5 b. 1.0 x 101 d. 5.0 ____ 31. Two resistors with values of 6.0 and 12 are connected in parallel. This combination is connected in series with a 2.0 resistor and a 24 V battery. What is the current in the 2.0 resistor? a. 2.0 A c. 6.0 A b. 4.0 A d. 12 A ____ 32. What is the current in the 8 resistor in the figure above? a. 1 A c. 3 A b. 2 A d. 6 A ____ 33. Three resistors with values of R1, R2, and R3 are connected in series. Which of the following expresses the total resistance, Rt, of the three resistors? a. Rt = R1 + R2 + R3 c. Rt = R1 = R2 = R3 b. Rt = (1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3) d. Rt =(1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3)–1 ____ 34. How much current is in one of the 10 resistors in the diagram shown above? a. 0.8 A c. 0.6 A b. 2 A d. 4 A Problems 35. The amount of charge that moves through the filament of a microwave in 10.0 s is 24.2 C. What is the current in the microwave? 36. The amount of charge that moves through an electric juicer in 36.0 s is 48.96 C. What is the current in the juicer? 37. The amount of charge that moves through the heating coils of a hair dryer in 50.0 s is 37.0 C. What is the current in the hair dryer? 38. A potential difference of 12 V is placed across a resistor with 0.25 A of current in it. What is the resistance of the resistor? 39. A potential difference of 20.0 V is placed across a resistor with 8.0 A of current in it. What is the resistance of the resistor? 40. A 2.0 k resistor has 0.042 A of current in it. What is the potential difference across the resistor? 41. A hair dryer is connected across a 120 V outlet. If the resistance of the hair dryer is 144 , how much power is dissipated in the form of electromagnetic radiation and heat? Chapter 19-20 Review Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. B C C C B A D A C C C D D C A B A A D D C D C A A D A C B B B A A A PROBLEM 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 2.42 A 1.36 A 0.74 A 48 2.5 84 V 1.00 x 102 W