* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Guinea Worm Disease
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
Kawasaki disease wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Schistosoma mansoni wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis research wikipedia , lookup
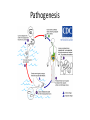
Guinea Worm Disease By: Daniel Coward Guinea Worm Disease • It is a preventable waterborne disease caused by a parasite Dracunculus medinensis • Also known as the “Guinea worm” Dracunculus medinensis • Also known as the “Guinea worm” • The largest tissue affecting parasite in humans Dracunculus medinensis • Also known as the “Guinea worm” • The largest tissue affecting parasite in humans • Adult female carries about 300 embryos Etiology • The disease is contracted when an individual drinks water that is contaminated with the parasite. Pathogenesis Pathogenesis Foot blister induced by the female guinea worm Guinea worm emerging Treatment • There is NO DRUG and no VACCINE to prevent infection Treatment • There is NO DRUG and no VACCINE for guinea worm disease to prevent infection • After the worm emerges, it can be pulled out very slowly Treatment • Many infected people get the worm out by twirling a stick Risk Groups • Occurs almost exclusively in isolated rural areas. Risk Groups • Occurs almost exclusively in isolated rural areas. • Occurs only in 5 countries in sub-Saharan Africa: Sudan, Ghana, Nigeria, Niger, and Mali. Risk Groups • In 2007, only 9,585 cases of GWD were reported. Most of those cases were from Sudan (61%) and Ghana (35%). Prevelance/Incidence • The disease occurs at two different times of the year Prevelance/Incidence • The disease occurs at two different times of the year • Near the Sahara the transmission occurs during the rainy season Prevelance/Incidence • The disease occurs at two different times of the year • Near the Sahara the transmission occurs during the rainy season • In the Savanna the transmission occurs during the dry season Why this matters? • The disease has a limited geographic distribution • It is seasonal in nature So? So? • It is easy to target and eradicate it from endemic areas Socioeconomic Effects • Estimated that infected people lose 100 days of work and children miss 25% of the school year Prevention • Guinea worm disease is a vulnerable disease because its transmission cycle relies on humans Prevention • Guinea worm disease is a vulnerable disease because its transmission cycle relies on humans • It is possible to permanently eliminate the disease with the use of prevention techniques Prevention • Filter water! Prevention • Educate! Prevention •Boil Water! Prevention • Only drink water from underground sources Eradication • Carter Center leads the way Eradication •Others Follow! Eradication • Educate Eradication • Educate • Treatment Eradication • Educate • Treatment • Larvicides Eradication • Educate • Treatment • Larvicides • Pond Caretakers Eradication Results Great!!! Eradication Results Great!!!