* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Understanding Networks
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
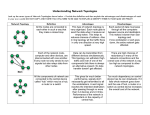
Understanding Network Topologies Look up the seven types of Network Topologies shown below – Provide the definition and then explain the advantages and disadvantages of each in your own words! DO NOT COPY AND PASTE! YOU WILL NEED TO BE ABLE TO EXPLAIN & IDENTIFY THESE IN YOUR QUIZ ON FRIDAY! Network Topology Definition In this form of network topology, all nodes are connected together to make a closed loop. Each device communicates with the two adjacent devices, and data travels around the network in one direction. Advantages Data traffic is very organized and only flows one way. No need for a network server to control connectivity. Each computer has equal access to resources. A few nodes are interconnected while Reduces network redundancy. the rest are connected between one or two other nodes. This causes some If the network fails there is still an devices to be indirectly connected. alternate path for it to flow. Disadvantages If one workstation goes down the entire network is affected. Each packet of data must pass through all the computers, creating a slow process. Can become costly if the network has many devices. Set-up and maintenance of this network is complex. Expansion is possible without disrupting the network. In this form of network topology all components are connected to a central device called a hub. New nodes can easily be added. Failure of one node does not compromise the entire network. Shorter process compared to the ring network topology. If the hub fails the entire network goes down. Performance is solely dependent on the capacity of the hub. Network Topology Definition In this form of network topology, all nodes are interconnected to each other. Advantages Can handle heavy traffic efficiency. If one node fails the network isn’t compromised. Disadvantages High cost. Extensive use of cables is required. Likelihood of network redundancies. In this form, each node is connected by a central cable, resulting in a start and endpoint. Expansion and modification can be made without affecting the network. Cheap to implement. Very simple to setup/maintain. If the cable or node fails, so does the network. Cannot handle high traffic. This is a combination of the bus and star network topology. The network starts at a hub, and then connects the other devices using cable, like the ones found in a bus network. Easy expansion of the network. Error detection and the implementation of solutions is easy. If one segment is damaged, the entire network does not fail. As more nodes are added, maintenance becomes difficult. This form is similar to the line network topology, but there are more endpoints, and branches are added to the cable. Simple to implement and maintain. If the cable fails, so does the network. Very Cheap. Cannot handle high traffic. Nodes share a common transition medium. Requires extensive use of cabling. Scalability of the network depends on the cable.