* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download thorax_diaphragm-1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
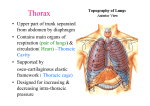
Thorax and Diaphragm OBJECTIVES: Thursday March 30th 2017 - List the parts of the sternum. - Name the different types of ribs and their parts. - Name and describe the importance of the inter‐costal muscles. - Name and describe the location of the inter‐costal nerves, arteries and veins. - Describe the innervation and vascularization of the diaphragm. -List the three major hiatuses and the vessels that go through each. Christopher Ramnanan, Ph.D. [email protected] PLEASE NOTE: These objectives will be tested on final practical but not next week’s midterm. (You’re welcome) Thoracic Cage: Sternum, 12 pairs of Ribs, 12 Thoracic Vertebrae Focus on The Sternum Jugular Notch Sternum: Manubrium Body Xiphoid Process Sum of 2 Costal Margins: Subcostal/Infrasternal Angle Note: Sternum articulates with ribs (via costal cartilages, sternocostal joints); manubrium makes up one boundary of the superior thoracic aperture Sternal Angle: 2nd Costal CartiIage T4/T5 IV Disc Bifurcation of Trachea Azygos Arch Aortic Arch (Lig. Arteriosum, L. Recurrent Laryngeal N.) The Thorax of Infants Before birth, the liver is a major hematopoetic organ. The liver is enlarged (relative to the anatomy of the adult), pushing the diaphragm up, and therefore making the thoracic cavity relatively small • Especially the pulmonary cavities/space occupied by the lungs Thoracic Cage: Focus on Ribs True Ribs (1-7): articulate w/ sternum via own costal cartilage False Ribs (8-10): articulate w/ sternum via costal cartilage of rib above it Floating Ribs (11-12): no articulation with sternum All ribs articulate with thoracic vertebrae posteriorly Features of a Typical Rib (3rd-9th ribs typical) Typical Ribs: -Head (2 articular facets to form joints with 2 thoracic vertebrae bodies) -Tubercle (1 articular site to form joint with thoracic vertebra transverse process) -Costal groove to convey intercostal neurovascular bundle Atypical Ribs (Superior Views) 1st rib: shortest; broadest; most sharply curved; grooves for subclavian vessels; one articular facet on head (T1 vertebrae) 2nd rib: short and broad; rough superior tuberosity Ribs 10-12: only one articular facet on head Ribs 11 and 12: short; no articulation with sternum Thoracic Cage: Focus on Vertebrae Costovertebral Joints (Example here: 7th rib) Intercostal Muscles Transversus Thoracis Innermost Intercostal M. ‘hands on chest’ External Intercostal M. ‘hands in pocket’ Internal Intercostal M. ‘hands on chest’ Note: These muscles are supplied by intercostal nerves, arteries, and drained by intercostal veins Inspiration Secondary SCM Scalenes Primary External intercostals Internal intercostals (interchondral part) Diaphragm Expiration Quiet breathing Passive recoil of lungs, rib cage Active breathing Internal intercostals (interosseous part) Abdominal muscles Intercostal Arteries and Veins Posterior Body Wall: Generally, Posterior Intercostal arteries supplied by thoracic aorta; Posterior intercostal veins drain to azygos system Anterior Thoracic Wall: Anterior intercostal arteries supplied by internal thoracic a.; Anterior intercostal vein drain to internal thoracic v. Posterior View, Ant. Body Wall Intercostal Nerves Anterior Rami of T1T11 Motor and Sensory supply to body wall (also supplies sympathetics) Courses laterally from sympathetic trunk Intercostal Nerve Intercostal Nerve Dermatomes Segmental Organization in Thorax T4 T5 T6 T7 T8 T9 T10 T11 T12 L1 Note: T4 and T10 landmarks The Diaphragm Central tendon Central tendon Diaphragm consists of central tendon (derived from cervical region in development) and lateral components (derived from body wall). Motor: supplied by C3-C5 Sensory: centrally C3-C5; peripherally T6-T12 The Diaphragm Diaphragm consists of central tendon (derived from cervical region in development, supplied by C3-C5) and lateral components (derived from body wall, supplied by T5-T12) Central tendon Central tendon Caval opening (T8) in central tendon: transmits IVC, right phrenic n., liver lymphatics Esophageal hiatus (T10): transmits esophagus and ant/post vagal trunks Aortic hiatus (T12): transmits aorta, thoracic duct, and azygos vein Origin: Ribs/Costal Cartilages, Sternum, Lumbar Vertebrae Insertion: Central Tendon Esophageal Hiatus Medial Arcuate Ligament: arc over psoas major (bilateral); sympathetic chains pass posterior to this ligament Lateral Arcuate Ligament: arc over quadratus lumborum (bilateral) Median Arcuate Ligament: arc over aorta (unpaired) R and L Diaphragmatic Crus: both crura form aortic hiatus and median arcuate lig.; right crus forms esophageal hiatus Blood Supply Pericardiacophrenic a/v (courses with phrenic nerves) Musculophrenic a/v (one terminal branch of the internal thoracic a/v) Superior and inferior phrenic arteries (off the aorta either above or below the diaphragm) LAB 5 CHECKLIST – THORAX AND DIAPHRAGM NB: Items italicized are conceptual, those denoted with a * are FYI THORAX - - Sternum Jugular notch Manubrium Body Xiphoid process Subcostal angle Sternocostal joints Superior thoracic aperture Sternal angle - 2nd costal cartilage - T4/T5 IV disc - Bifurcation of the trachea - Azygos arch - Aortic arch - Lig. Arteriosum - L. recurrent laryngeal n. MUSCLES Transversus thoracis m. External intercostal m. Internal intercostal m. Innermost ntercostal m. Diaphragm - Caval opening - Esophageal hiatus - Aortic hiatus - Medial arcuate ligament - Lateral arcuate ligament - Median arcuate ligament - R and L diaphragmatic crus - - BONES AND JOINTS True ribs (1-7) False ribs (8-10) Floating ribs (11-12) Head of rib Neck of rib Tubercle Costal angle Body Costal groove Typical rib Atypical rib Vertebrae - Superior costal facet - Inferior costal facet - Facet for tubercle - Spinous process - Transverse process - Lamina - Body - Vertebral foramen Costovertebral joint Costotransverse joint INNERVATION - Intercostal n. - Phrenic n. - Motor and sensory supply to the diaphragm - ARTERIAL SUPPLY Anterior and posterior intercostal a. Internal thoracic a. Thoracic aorta Pericardiacophrenic a. Musculophrenic a. Superior phrenic a. Inferior phrenic a. - VENOUS DRAINAGE Anterior and posterior Intercostal v. Azygos system Internal thoracic v. Pericardiacophrenic v. Musculophrenic v.