* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download highly unlikely
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Introduction to probability
Every day we ask questions such as ‘Is it going
to rain today?’,
‘Will my football team win this weekend?’ or
‘Will I be selected to be the captain of the Year 9
class?’.
These scenarios are affected by many different
variables,
which could include the location of rain clouds,
the players injured on the football team
Probability is the likelihood or chance of an event
occurring or not occurring.
There are times when we can be certain about a
specific event.
For example, it is certain that you will not attend
school on Christmas Day.
The probability of attending school on Christmas Day
is assigned a value of 0, representing an impossible
outcome.
Most events lie between these two extreme
probabilities of 0 and 1 and are assigned a probability
in this range, as shown by this probability scale.
Words often used to discuss the chances of
something occurring are: impossible, highly unlikely,
unlikely, even or fair chance, likely, highly likely,
certain.
An event that has a probability of 1 is defined as
certain.
An event that has a probability of 0 is defined as
impossible.
An event that has a probability of 0.5 is defined as an
even chance.
As the probability gets closer to 0, the chance of
something occurring is decreasing.
As the probability gets closer to 1, the chance of
something occurring is increasing.
Words often used to discuss the chances of something
occurring are: impossible, highly unlikely, unlikely,
even or fair chance, likely, highly likely, certain.
These words can be placed at approximate places on
the probability scale.
On the probability scale , insert the events at
appropriate points.
You will sleep tonight.
Solution
You will come to school the next Monday during a
school term.
Solution
It is very likely but not certain that I will come to
school on a Monday during term.
It will snow in Victoria this year.
It is highly likely but not certain that it will snow in
Victoria during winter.
The chance of snow falling in Victoria in summer is
highly unlikely but not impossible.
Example
A die is rolled. Indicate whether the outcomes are
equally likely.
Even numbers and odd numbers
Solution
Even numbers: 2, 4, 6
Odd numbers: 1, 3, 5
The outcomes: even numbers and odd numbers are
equally likely, as they each have three results.
A die is rolled. Indicate whether the outcomes are
equally likely. Factors of 6 and factors of 4
Solution
Factors of 6: 1, 2, 3, 6
Factors of 4: 1, 2, 4
The outcomes: factors of 6 and factors of 4 are not
equally likely, as they have a different number of
results.
Are you ready pg- 553 question no 1,2,3,4,5 & 6
Ex 13 A question no 1 & 2
Sample space
Any probability experiment has a finite number of
possible outcomes.
The set of possible outcomes is called the sample
space, and is usually represented by the symbol S.
When a coin is tossed, The sample space is written as
S = {H, T}.
Similarly, when a die is rolled
S = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}.
A sample space (S) is the list of all the possible
outcomes obtained from an experiment.
For two-step or multiple-step experiments, such as
tossing two different coins, or tossing a coin and
rolling a die, the sample space is more complex.
Two way table
Tree Diagram
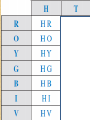
A coin is tossed, then a circular spinner with seven
equal sectors labelled R O Y G B I V is spun.
Display all possible outcomes in a two-way table, then
list the sample space for this experiment.
Solution
Ex -13A
Question no 3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12, & 13