* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circuit Analysis
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
War of the currents wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
General Electric wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Electric motorsport wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
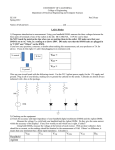
Name _______________________ Measuring E-Fields in Conductive Paper The purpose of this assignment is to introduce 2 new tools and strengthen understanding about the connection between electric fields and electric potential. I. The Power Supply Our Extech Power supplies have digital Voltage readings of Voltage and Current output. When using the power supplies, Current A. the power should remain off until the circuit is completed. B. the voltage output should be set to 0.0 V C. the current output should be set to ½ maximum Ground +V When the circuit is complete, then A. turn the power on B. slowly increase the voltage to the desired setting C. turn the power off if the current goes too high or if there is smoke or you smell something burning. II. The Digital Multimeter (DMM) The DMM is a powerful tool that can make many kinds of measurements. We will be measuring potential difference or voltage in this activity. Move the selector to 20 V (or 200 V). Switch from Alternating Current to Direct Current Screen Tilts Up On/Off Range for Voltage Range for Resistance 20 V Range for Current Red Lead Stays Here for Voltage and Resistance Measurements Red Lead Moves Here for Current Measurements 10 A DMM probe 2 A or less DMM ground lead III. Experiment Part 1 – 20 cm Strip @ 10V Connect the power supply leads as shown above and apply 10 V to each end of the 20 cm strip. Distance above Ground (cm) Electric Potential (V) Place the 20 cm strip on a piece of cardboard. Connect the DMM ground lead on the ground end of the carbon strip. Place the DMM probe at the appropriate distance on the carbon strip and measure the electric potential for each distance above ground. Electric Field Strength (V/m) Distance above Ground (cm) 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 Plot the electric potential as a function of position on the attached graph paper. Calculate the average electric field strength: E V V V 2 1 x x2 x1 Part 2 – 6 cm Strip @ 10V Repeat the steps above for the 6 cm strip. Electric Potential (V) Distance above Ground (cm) Electric Field Strength (V/m) Distance above Ground (cm) 6 5 4 3 2 Part 3 – 6 cm & 14 cm Strip @ 10V Repeat the steps above for the 6 cm strip and 14 cm strip connected sequentially with a connecting lead. Distance Electric Field Distance Electric above Ground Strength above Ground Connect the power supply Potential (V) (cm) (V/m) (cm) leads as shown above and 20 19 apply 10 V to each end of the connected strips. 18 17 Place the strips on a piece of cardboard. Connect the DMM ground lead on the ground end of the carbon strip. Place the DMM probe at the appropriate distance on the carbon strip and measure the electric potential for each distance above ground. 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 Plot the electric potential as a function of position on the attached graph paper. Calculate the average electric field strength: Connecting lead E V V V 2 1 x x2 x1 Part 4 – Conclusions 1. How is the electric field strength reflected by the graph above? 2. What happens to the electric potential of the charges as they migrate through the conductive paper? 3. What is the potential difference of the charges between the ends of the connecting alligator lead in part 3?