* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pathogenicity and virulence
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Cross-species transmission wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
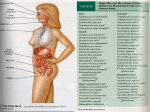
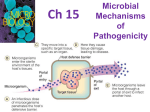
Pathogenicity and virulence Virulence factors of bacteria Virulence • Microorganisms cause resulting in human diseases • Disease causing microorganisms possess virulence factors. • Virulence factors are properties of pathogens to overcome the host defenses and to establish an infection and cause disease. Virulence factors • 1. Adhesion factors – Capsules, slime layers, surface carbohydrates, proteins, flagella and pili aid in attachment. • 2. Invasiveness • enzymes that enhance invasiveness by enabling the microorganisms to destroy body tissue and cells. Eg. Hyluronidase, collagenase etc. • 3. Toxicity – Pathogens produce toxins, that disrupt the normal functioning of the body. Classified into Endotoxins and exotoxins. – Intoxications are diseases that result from the entrance of a specific toxin into the host body. Toxins • Exotoxins : Exotoxins are soluble heat-labile proteins that are released as the bacteria grow – Examples: i. Neurotoxin – Botulinum toxin – ii. Cytotoxin – Haemolysin – iii. Enterotoxin – Cholera toxin • Endotoxins: – Most Gram negative bacteria have lipopolysaccharides (LPS) in their outer membrane of their cell envelope. LPS is toxic to specific hosts. Diseases Classification and Glossary • • • • • • • Endemic disease Epidemic Pandemic Epidemiology Zoonoses Nosocomial infections Types of Disease – Acute disease – Chronic Disease Process • Patterns of disease – Signs and symptoms • Stages of a disease – Incubation – Prodromal stage – Period of illness – Period of decline – Full recovery Transmission of infectious agents • Portals of Entry – – – – Respiratory tract Gastro intestinal tract Genitourinary tract Skin and wounds and paraenterel routes • Transmission is effected by – Direct contact transmission – Direct faecal – oral route – Indirect contact transmission • Portals of exit – Pathogens of gastrointestinal and genitourinary systems exit through body fluids or faeces – Pathogens of respiratory systems exit through nose, mouth fluids – during coughing, sneezing and speaking Diseases of the respiratory systems • • • • Pharyngitis or sore throat Pneumonia Diphtheria – Corynebacterium diphtheria Tuberculosis – Mycobacterium tuberculosis Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract • • • • • Staphylococcal food poisoning -Staph aureus Salmonellosis-Salmonella Shigellosis Travelers' diarrhea Other gastroenteritis Diseases of Central Nervous System • A. Meningitis - Neisseria meningitis, Haemosphilus influenza • B. Tetanus - Clostridium tetani • C. Botulism - Clostridium botulinum Diseases of the cardiovascular and lymphatic system • Septicemia or blood poisoning E.coli, Pseudomonas qeruginosa, Proteus sp etc., • Typhoid fever – Salmonella typhi • Plague – Yersinia pestis Diseases of the Urino-genital tract • Urethritis and cystitis – E.coli, Klebsiella Enterobacter, Proteus, Pseudomonas etc., • Leptospirosis – Leptospira interrogans • Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae • Syphillis – Treponema palladium Fungal human Diseases • Diseases of the respiratory tract – Histoplarma Capsulatum, Coccidioides immitis Aspergillus • Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract – Aspergillus sp. • Diseases of Vaginal tract – by Candida • Diseases of central nervous system – Ergotism - by Claviceps purpurea – Meningitis - Cryptococcus neoformans • Diseases of the skin • Dermatomycosis - Trichophyton • Asporotrichosis - Sporothrix Diseases caused by Protozoa and Parasites • • • • Amoebiosis - Entamoeba histolytica Vulvovaginitis - Trichomonas vaginalis Trypanosomiaris - Trypanosoma gambiense Malaria - Plasmodium (transmitted by mosquitoes) • Parasitic Diseases – Tapeworms, Elephantiasis, Schistosomiasis