* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Advanced Arduino – Robot – Presentation
Control theory wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Fade (audio engineering) wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
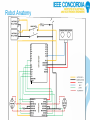
Microprocessors Tutorial 2: Arduino Robotics Agenda 1. Robot Anatomy 2. Sensor Review 3. PWM 4. MAKE: Fade 5. Motors 6. H Bridge 7. Robot Control library 8. MAKE: Robot react 9. Challenge: Solve Maze 10. Links Robot Anatomy Robot Anatomy Sensor Review • Analog Arduino mapping: 0-5V 0-1023 • 3 connections: V+, pin, GND • Serial Monitor: • Use Serial.begin(9600) to start communication • Use custom function serialOutputValue(“msg”, value) to see sensor value in serial monitor • This robot has IR range sensor: Outputs 0.0 - 2.6V (0-600 in Arduino) Peaks at 15cm, farther objects create lower voltage BUT code inverts relationship! Pulse Width Modulation • Duty cycle = percentage of time signal is positive in square wave • Min-Max voltage: 0 – 5v Min-Max Arduino mapping: 0 – 255 • PWM pins have a ~ on Arduino 10% average 50% average 90% average Make: Fade • Use analogWrite(pin, value) to fade light on/off using for loop to vary value • Remember PWM range is 0-255 • Recall LED connection: long leg = positive small resistor in series necessary Challenge: Fade Increments • Use PWM to 1. fade the led from 0 to full in 5 seconds, 2. hold for 2 secs, 3. fade back down in 7 seconds. • Then each loop would do it faster and faster or brighter and brighter! Motors • They draw more current than USB/Arduino can supply (40mA per pin, 200mA in total) so need another power supply: batteries • Current through in 1 direction turns them in 1 direction • More voltage = More speed, how to control voltage? • Use electronically controlled switch (transistor) between motor and batteries • Use PWM pin to control switch • Motors in this robot run on 4.5-7.0V and have a peak current of 1A. H- Bridge • Used to make 1 motor turn in either direction by directing current • use 4 switches controlled by 2 signals H- Bridge • The IC we will use (SN754410N) has 2 H-Bridges to control 2 motors • PWM is used here at the enable pin to control speed A CHALLENGE: solve the maze! Create your own algorithm to beat the maze using Example 0: Template Or start from our other example codes Example 4, 5, 6 Useful Links Arduino Examples http://arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/HomePage MAKE projects http://makezine.com/arduino/ http://makezine.com/category/electronics/arduino/?post_type=pr ojects Jeremy Blum Tutorials (#5: motors and transistors) http://www.jeremyblum.com/category/arduino-tutorials/ Questions? Comments? Suggestions? [email protected] ieee.concordia.ca