* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EE 330 LAB Report #5
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
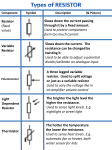
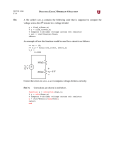
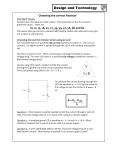
2012 Iowa State University Che, Xiaoyu [EE 330 LAB REPORT #5] Lab 5: Creating Bonding Pads August 31, 2012 [EE 330 LAB REPORT #5] Introduction In this lab we will create a resistor in the layout view and also investigate the design of a basic bonding pad and simple ESD protection circuitry. The protection circuitry as well as the human body model will be drawn in schematics and then realized in layout view. Steps 1. Layout of a resistor a. b. c. d. Calculate the width of the resistor to minimize it. Draw the resistor with poly. Attach via, metal and res_id layer. Check whether the resistance is accurate. If not, make some adjustment. 2. Layout of a bonding pad Create a bonding pad comprised of stacked layers of metal1, metal2, metal3 with a pad opening with the glass layer. Use the appropriate stacked vias to interconnect these metal layers. Use the maximum possible number of vias to connect two adjacent metal layers. The pad should meet design rules and the opening in the glass layer is to be 78µm x 78µm, but as small as possible. 3. Pad Protection Circuitry a. Create a schematic of the ESD protection circuit. b. Create a layout of the ESD protection circuit. c. Diodes: p+ and n+ diffusions inside an n-well. 4. Human Body Model Create a human body model according to the figure. Set the starting voltage of the charged capacitor in different numbers and simulate the circuit to see the output voltage. Iowa State University |Xiaoyu Che 1 August 31, 2012 [EE 330 LAB REPORT #5] Lab Result: Figure 1&2: Resistor Analysis: This is the resistor created with poly. After calculation I get that it should be 10 rows if the length and width are the same. But when it was created I found the resistance to be a litter bigger so I made some adjustment. Iowa State University |Xiaoyu Che 2 August 31, 2012 [EE 330 LAB REPORT #5] Figure 3&4: Bonding pads Analysis: The figure shows the bonding pads with 3 layers of metal and the glass. The vias can be seen everywhere on the pad which are very compact. The size of glass is 78µm x 78µm while the size of pad is 96µm x 96µm. They do satisfy the rules. Iowa State University |Xiaoyu Che 3 August 31, 2012 [EE 330 LAB REPORT #5] Figure 5: Schematic of the protection circuitry Iowa State University |Xiaoyu Che 4 August 31, 2012 [EE 330 LAB REPORT #5] Figure 6&7: layout of the protection circuitry Analysis: This is the layout of the protection circuitry. In the diodes, the p+ and n+ rectangles are attached to each other and both in the n well and dio_id layer. The diodes can be recognized in extraction and LVS. The figure shows that the LVS is successful. Iowa State University |Xiaoyu Che 5 August 31, 2012 [EE 330 LAB REPORT #5] Figure 8: Schematic of the human body model Figure 9-17: Output voltage with different input voltages Time scale: 5us Iowa State University |Xiaoyu Che 6 August 31, 2012 [EE 330 LAB REPORT #5] 250v: 500v: 1000v: 2000v: Iowa State University |Xiaoyu Che 7 August 31, 2012 4000v: [EE 330 LAB REPORT #5] 8000v: 10000v: From the figures we know that for every input the output voltage is always bigger than 5v. So the circuit is unsafe. If we change the standards, for example, the voltage below 8v won’t destroy the circuit, we can say that the device belongs to class 1c. Iowa State University |Xiaoyu Che 8 August 31, 2012 [EE 330 LAB REPORT #5] Conclusion This time we learnt the procedure of creating a resistor in layout. Calculation is needed before drawing and adjustment is also necessary after drawing. We also created a bonding pad and a ESD protection circuitry and then ran the simulation to see the voltage of the output and whether this voltage is OK. Iowa State University |Xiaoyu Che 9