* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transformers
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
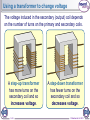
Transformers 1 of 6 © Boardworks Ltd 2012 Parts of a transformer 2 of 6 © Boardworks Ltd 2012 Using a transformer to change voltage The voltage induced in the secondary (output) coil depends on the number of turns on the primary and secondary coils. A step-up transformer has more turns on the secondary coil and so increases voltage. 3 of 6 A step-down transformer has fewer turns on the secondary coil and so decreases voltage. © Boardworks Ltd 2012 Investigating transformers 4 of 6 © Boardworks Ltd 2012 Properties of transformers Transformers transfer power between circuits. The design of a transformer determines the characteristics of the electricity flowing in its secondary circuit. The frequency of the alternating current in the secondary circuit matches the primary circuit, but what about voltage? In an ideal transformer, the voltage in each circuit is related to the number of coils on each side by the following formula: primary voltage secondary voltage Vp Vs 5 of 6 = primary turns secondary turns = Np Ns © Boardworks Ltd 2012 Calculating voltage 6 of 6 © Boardworks Ltd 2012