* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Network Architecture
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Bus (computing) wikipedia , lookup
Passive optical network wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Registered jack wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
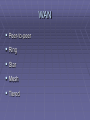
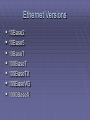
Network Architecture Layout designed and constructed by: Vicki Kertz TOPOLOGIES Bus Ring Star Hybrid Enterprise-wide WAN Bus a central cable that connects all devices on a local-area network Ring Each node is connected to the two nearest nodes so that the entire network forms a circle. Star Each node (file server, workstations, and peripherals) connected directly to a central network hub or concentrator Hybrids Star-wired Ring Star-wired Bus Daisy-chained Hierarchical Enterprise -wide Backbone Networks – cabling that connects the hubs, switches and routers Serial – simplest; two or more connected by a single cable Distributed – number of hubs connected to a series of central hubs in a hierarchy Collapsed – a router or switch as the single central connection point for multiple subnetworks Parallel – robust; more than one connection from the central router to each network segment Mesh – routers interconnected with others and at least two pathways connecting each router WAN Peer-to-peer Ring Star Mesh Tiered Network Transport Systems The logical topology is the way that the signals act on the network media, or the way that the data passes through the network from one device to the next without regard to the physical interconnection of the devices. Switching Circuit - A type of communications in which a dedicated channel (or circuit) is established for the duration of a transmission. Message – establishes a connection between two devices, transfers the info to the 2nd device, then breaks the connection. Packet - Refers to protocols in which messages are divided into packets before they are sent. Each packet is then transmitted individually and can even follow different routes to its destination. Once all the packets forming a message arrive at the destination, they are recompiled into the original message. CSMA/CD Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection Set of rules determining how network devices respond when two devices attempt to use a data channel simultaneously (called a collision) Standard Ethernet networks use CSMA/CD Ethernet Versions 10Base2 10Base5 10BaseT 100BaseT 100BaseTX 100BaseVG 1000BaseX 10Base2 The 10Base-2 standard (also called Thinnet) uses 50 ohm coaxial cable (RG-58 A/U) with maximum lengths of 185 meters. Ethernet over coaxial cable with a maximum distance of 185 meters. Also referred to as Thin Ethernet or Thinnet or Thinwire. 10Base5 The original cabling standard for Ethernet that uses coaxial cables. The name derives from the fact that the maximum data transfer speed is 10 Mbps, it uses baseband transmission, and the maximum length of cables is 500 meters. 10BaseT 10 Mbps baseband 100BaseT A networking standard that supports data transfer rates up to 100 Mbps (100 megabits per second). 100BASE-T is based on the older Ethernet standard. Because it is 10 times faster than Ethernet, it is often referred to as Fast Ethernet. (100BaseTX & 100BaseT4) 1000BaseT A specification for Gigabit Ethernet over copper wire (IEEE Std. 802.3ab). The standard defines 1 Gb/s data transfer over distances of up to 100 meters using four pairs of CAT-5 balanced copper cabling and a 5-level coding scheme. Other 1000Base-T benefits include compatibility with existing network protocols (i.e. IP, IPX, AppleTalk), existing applications, Network Operating Systems, network management platforms and applications. Switched Ethernet An Ethernet LAN that uses switches to connect individual hosts or segments. In the case of individual hosts, the switch replaces the repeater and effectively gives the device full 10 Mbps bandwidth (or 100 Mbps for Fast Ethernet) to the rest of the network. Ethernet Frame Types 802.2 802.3 Ethernet II Ethernet SNAP 802.2 General standard for the data link layer in the OSI Reference Model. The IEEE divides this layer into two sub layers -- the logical link control (LLC) layer and the media access control (MAC) layer. Preamble 8 bytes Destination address Source address Length 2 bytes LLC FCS 46 – 1500 4 bytes bytes SSAP 1 byte DSAP 1 byte Control Field 1 byte 802.3 Defines the MAC layer for bus networks that use CSMA/CD. This is the basis of the Ethernet standard Destination address Preamble 7 bytes SFC 1 byte Source address Length 2 bytes LLC 46 – 1500 bytes FCS 4 bytes Mau Multistation Access Unit a token-ring network device that physically connects network computers in a star topology while retaining the logical ring structure MAU is a special type of hub One of the problems with the token-ring topology is that a single non-operating node can break the ring. The MAU solves this problem because it has the ability to short out non-operating nodes and maintain the ring structure Design Considerations for Token Ring Networks Cabling Connectivity devices # of stations Speed Scalability Topology /sbin/init 0