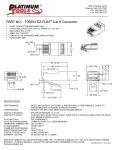
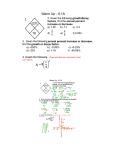
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Prerequisite Skills Solving for x with absolute values Get rid of the
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Factorization wikipedia , lookup
System of linear equations wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
History of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental theorem of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Cubic function wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Prerequisite Skills A. Solving for x with absolute values Get rid of the absolute value signs by 1. setting everything within absolute value to the opposite 2. keeping the original equation Solve per usual B. Simplifying with square roots in the denominator Multiply the top and bottom by the square root on the bottom The square root number is no longer a square root and becomes the “normal” form Reduce square roots to simplest form Solve per usual Chapter One Skills A. Finding the formula for f^-1(x) Switch the x and y values and solve per usual B. Altering graphs If f(x) is a function… f(x)-1 graph is shifted down one unit f(x)+1 graph is shifted up one unit f(x-1) graph is shifted right one unit f(x+1) graph is shifted left one unit f(-x) graph is reflected across the xaxis C. Odd and Even functions A parabola is an even function A curve is an odd function A negative function will be flipped over A positive function is “normal” D. Function Inception XD For (f o g)(x), plug in the “g” equation in for x in the f equation For (fg)(x) multiply the f equation by the g equation Chapter Two Skills A. Writing linear equations to satisfy given conditions Find the slope of the line using (y2y1)/(x2-x1) Plug the in the slope and a coordinate pair into the equation y-y1=m(x-x1) Solve as per usual B. Finding the vertex and axis of a graph If not in quadratic form, unfoil Find “h” with –(b/2a) THIS IS THE AXIS! Plug in “h” for all “x” values in the equation and solve to find “k” (h,k) is the vertex of the parabola C. Writing an equation for the quadratic function to satisfy a given vertex and point Plug in the vertex values for h and k. y=a(x-h)+k Plug in x and y values to solve for a Plug in a into first equation D. Remainder Theorem If you plug the dividend into the divisor, the solution will be the remainder for the quotient E. Factor Theorem If you plug in the x value into the equation and the solution is zero, the first polynomial is the factor of the second F. Qudratic Equation G. Completing the square Take middle term and divide by 2 Square the quotient above Take out the middle equation, add the squared thing to both sides Since the left side is to the second power, take the square root of both sides H. When Finding the Real Zeros of a Function… An= based off of the leading coefficient Ao= based off of the last number Find the factors of AN and AO. Use the factors of AO over AN to find possible zeros. Once you find a zero, do synthetic division with that number, rewrite the equation as a quadratic, and solve with the quadratic formula. To write in linear factorization, do (xn)… I. Finding Asymptotes and Intercepts Y-Intercept: plug in 0 for x-values and solve X-intercept: set the numerator to zero and solve Vertical Asymptote: set the bottom to zero Horizontal Asymptote: compare coefficients -if top and bottom x^ values are equal, then the top divided by the bottom is the asymptote - if the top x^ value is greater than the bottom, there is NO asymptote - if top x^ value is less than the bottom, the asymptote is 0 Chapter Three A. Exponential Growth vs. Decay USE CALCULATOR B. Evaluating logarithmic functions without a calculator logxY is really asking… x elevated to what power will give me y natural logs come in base 10 pairs C. Rewriting Logarithms as Exponents Log3x=5 35=x