* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Explain and enumerate the different classifications
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
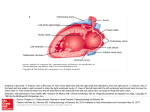
1) Explain the process of pulmonary and systemic circulations pathway of blood flow through the heart. Ans 2) Explain and enumerate the different classifications of cardiovascular disease ? 1) Conduction disorders(Dysthymias) Supraventricular rhythms Ventricular dysrhythmias Atrioventricular conduction block Ventricular conduction block 2) myocardial disorders(coronary heart disease) Angina pectoris Acute myocardial infection Sudden cardiac death 3) structural disorder Valvular heart disease Cardiomyopathy Infection disorder 3. Give the pathophysiology, sign and symptoms, and nursing care for the following disorder Inflammatory Hear ? Pathophysiology Sign/symptom Nursing care Disease Rheumatic fever/ -Rheumatic fever -Fever Example: Diet rheumatic heart disease occurs equally in -Painful and tender -No specific dietary both sexes and at joints recommendation exists. all ages, but it is -Red, hot or swollen CHF may require salt more common in joints restriction. children with the -Small, painless Activity peak incidence bumps (nodules) -Bed rest is a time- occurring between beneath the skin honored part of ARF Endocarditis ages 5 and 15 -Chest pain therapy and is especially years. -Heart murmur important in those with -Fatigue carditis and other. Abstract -Fever and chills -Monitor vital sign hourly if -Infective -Fatigue Patient condition unstable. endocarditis (IE) is -Aching joints and -Monitor central venous an uncommon muscles pressure if central line infection, occurring -Night sweats present. as a complication in -Shortness of breath -Monitor intake output varying -Paleness hourly. percentages of -Persistent cough -Monitor weight daily. bacteremic -Swelling in your -Assess neurological episodes. The feet, legs or status hourly. ability of an abdomen organism to cause -Unexplained weight endocarditis is the loss. result of an interplay between the predisposing structural abnormalities of the cardiac valve for bacterial adherence. Myocarditis 1) direct invasion to -Shortness of breath -Give a comfortable the infarction. during exercise, position (semi-fowler 2) Process -Fatigue, position). immunologically Palpitations light -Give O2 supplement and against infarction. headedness, ensure saturation ˃90%. 3) Remove the -Irregular heartbeat, -Give drugs as indicated toxins that damage Sudden loss of (Aspirin, Steroids). the myocardium. consciousness, -Give anti pyretic drug if -Fever fever present. -Bluish or Grayish discoloration of the skin. -Fluid retention with swelling. Pericarditis - The pericardium -Sharp, piercing Abstract consists of a 2- chest pain over the -Nursing care of the layered pliable, fibro center or left side of patient with pericarditis, a serous sac that the chest commonly seen syndrome covers the surface -Shortness of breath in the clinical setting, is of the heart. The when reclining discussed in this article. inner layer, the -Heart palpitations Pericarditis is particularly visceral Low-grade fever prevalent in the patient pericardium, is -An overall sense of following myocardial adherent to the weakness, fatigue or infarction. myocardium. feeling sick -Cough -Abdominal or leg swelling Valvular heart Pathophysiology Sign/symptom Nursing care disease Mitral stenosis -The normal area of the -Heart failure -Before giving penicillin, ask mitral valve orifice is -Palpitations the patient if she’s ever had about 4 to 6 cm2. In -Chest pain a hypersensitivity reaction to normal cardiac physiology, the mitral valve opens during left -Hemoptysis -Thromboembolism the drug. -Assist the patient with bathing as necessary. ventricular diastole, to -Allow the patient to express allow blood to flow from his concerns over being the left atrium to the left unable to meet her ventricle. responsibilities because of activity restrictions. -Place the patient in an upright position to relieve dyspnea, if needed. Mitral regurgitation -MR can be caused -Dyspnea -Assess mental status by organic disease -Fatigue (Restlessness, severe (eg, rheumatic fever, -Orthopnea anxiety and confusion). ruptured chordae -Pulmonary edema -Check vital signs (heart tendineae, (often the initial rate and blood pressure). myxomatous manifestation) -Assess heart sounds, degeneration, leaflet perforation) or a functional abnormality. noting gallops, S3, S4. Mitral Valve Prolapse -In mitral valve -fatigue, -If dysrhythmias are prolapse, a portion of shortness of breath documented and cause a mitral valve leaflet -light-headedness symptoms, the patient is balloons back into the -dizziness atrium during systole. -syncope Rarely, the ballooning -palpitations Aortic stenosis stretches the leaflet -chest pain and to the point that the anxiety advised to eliminate caffeine and alcohol from the diet and to stop smoking; antiarrhythmic medications may be prescribed. -Chest pain that does not valve does not respond to nitrates may remain closed during respond to calcium channel systole. blockers or beta-blockers. -Describe the -Breathlessness -Assist the patient in pathophysiology of -Chest pain (angina), bathing, if necessary aortic stenosis pressure or tightness -Offer diversional activities -Fainting, also called that are physically -Identify clinical syncope undemanding. manifestations of -Palpitations or a -Alternate periods of rest aortic stenosis feeling of heavy to prevent extreme fatigue -Decline in activity and dyspnea. -Discuss medical and nursing managemen level Aortic regurgitation Tricuspid stenosis -Incompetent closure -weakness, fainting, -you have a fever. of the aortic valve can or swollen ankles and -You feel more tired than result from intrinsic feet. usual. disease of the -chest pain -You are more short of leaflets, cusp, -fatigue breath than usual when diseases of the aorta, you exercise or lie down or trauma. Diastolic You cough more than reflux through the usual, especially when aortic valve can lead you lie down. to left ventricular -You are pregnant or think volume overload. you are pregnant. -Tricuspid stenosis -tired and lethargic -Assess mental status results from -fragility (Restlessness, severe alterations in the -a quivering feeling in anxiety and confusion). structure of the the neck -Check vital signs (heart tricuspid valve that -a rapid, irregular rate and blood pressure). precipitate heartbeat called a -Assess heart sounds, inadequate excursion palpitation, or both. noting gallops, S3, S4. of the valve leaflets. -pain in the upper The most common right part of their etiology is rheumatic abdomen which may fever, and tricuspid be caused by an valve involvement enlarged, congested occurs universally liver. with mitral and aortic valve involvement. Tricuspid regurgitation Abstract -Shortness -Assess mental status -Tricuspid regurgitation -Weakness or (Restlessness, severe (TR) is one of the most dizziness, anxiety and confusion). commonly encountered -Wheezing and heavy -Check vital signs (heart valvular problems in coughing, rate and blood pressure). clinical practice. -Physical exertion, -Assess heart sounds, Although diagnosed -Palpitations mild - noting gallops, S3, S4. easily with chest pain, echocardiography, it -Fever, contributes to significant -Rapid weight gain, mortality and morbidity -Swelling of the when severe. ankles, feet or abdomen pulmonic stenosis -PS can be due to -Heart murmur -Cath lab interventional isolated valvular (90%), -Shortness of breath, procedure. subvalvular, or especially during -Surgical repair. peripheral exertion -Ventilator. (supravalvular) -Chest pain -Intravenous (IV) obstruction, or it may be -Loss of catheters. found in association consciousness -Arterial line. with more complicated (fainting) -Nasogastric (NG) tube. congenital heart -Fatigue -Urinary catheter. disorders. Pulmonic -Incompetence of the -Fatigue -In addition, stay alert for regurgitation pulmonic valve occurs shortness of breath, conditions that can impair by 1 of 3 basic especially during O2 delivery, such as pathologic processes: exertion elevated temperature, dilatation of the -chest pain anemia, impaired cardiac pulmonic valve ring -palpitations output, acidosis, and -enlarged liver sepsis. -fainting with exercise -exercise intolerance