* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download population - Northwest ISD Moodle
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
The Population Bomb wikipedia , lookup
Two-child policy wikipedia , lookup
Human overpopulation wikipedia , lookup
World population wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
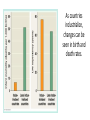
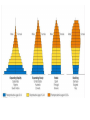
Check on your plants, make observations for today. BECAUSE our plants are progressing a little slower than they should, make another data table…hopefully next week our plants will be where they need to be in order to move to the next step in this lab. This is 4/19/17, Day 19 since we planted them. Bell-ringer 4/20 1. What is the difference between innate and learned behavior? 2. How does altruistic behavior lead to survival and reproductive success? GET OUT YOUR ECOLOGY READING ECOLOGY The study of organism interactions with each other and with their environment. Each level of organization emerges from the processes of the level below it. organism population A group of organisms of the same species that are in the same area at the same time. community ecosystem biome How are populations structured? Organisms enter a population in one of two ways… Organisms leave a population in one of two ways… Population Density: Population Dispersal The number of individuals per unit area in a population. The pattern of spacing among individuals in a population. Not static- changes as individuals are added or removed. Population Growth Exponential Model: -Measures population increase under ideal conditions. -Increase at a constant rate, resulting in a ‘J’ shaped curve when plotted over time. -Rarely occurs in nature for long, but can be characteristic of populations introduced to new environments or rebuilding from a catastrophic event. - Studying this reveals the capability of growth and conditions which this type of growth may occur. Population Growth Logistic Model: -Takes into account that as populations increase, resources become more limited. - Each population has a carrying capacity: maximum population size that a particular environment can sustain. S-Curves • Limiting factors are any biotic or abiotic factor that can Limiting determine Common Factors the carrying capacity of a population in a given area. • Density-dependent • Density-independent Density-Dependent Factors • Limiting factors that depend on population size • Density-dependent factors become limiting only when population density reaches a certain level • So as a population’s density increases, these are mechanisms that slow or stop growth by decreasing birth rates or increasing death rates. Examples: Competition for resources Predation Space Contagious disease Density-Independent Factors • Limiting factors that affect populations regardless of their size Examples: Natural disasters Unusual weather (drought) Human activities (damming rivers/cutting forests) In nature, there is a trade-off in populations between reproduction and survival. Populations based on Survivor Rates • K-selected species • Operates in populations living at densities near the limit imposed by their resources (carrying capacity, K)/ competition among individuals is stronger. • Few offspring per pregnancy (less offspring per capita) • Invest a lot in raising offspring (higher survival rates) • Primates/Elephants • Coconut/Brazil nut trees K-selected Populations based on Survivor Rates • r-selected • Operates in populations that are well below carrying capacity or individuals face little competition. • These maximize ‘r’- the per capita rate of increase • many offspring • little parental care • • • • insects Many plants Algae bacteria r-selected Human Population Growth • About 500 years ago, the human population began growing more rapidly because of agriculture and industry. • With these advances, the human population experienced exponential growth • That growth rate is slowing…. This decrease in growth rate is not uniform across the globe…. As countries industrialize, changes can be seen in birth and death rates.