* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exercise A
Multidimensional empirical mode decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Electronic music wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Electrical engineering wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Computer program wikipedia , lookup
Electronic musical instrument wikipedia , lookup
Hendrik Wade Bode wikipedia , lookup
Music technology (electronic and digital) wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
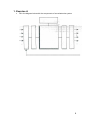
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ Ανώτατο Εκπαιδευτικό Ίδρυμα Πειραιά Τεχνολογικού Τομέα Τίτλος Μαθήματος Ενότητα: Mechatronics Παναγιώτης Τσατσαρός Τμήμα Μηχανολόγων Μηχανικών ΤΕ Άδειες Χρήσης • Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό υπόκειται σε άδειες χρήσης Creative Commons. • Για εκπαιδευτικό υλικό, όπως εικόνες, που υπόκειται σε άλλου τύπου άδειας χρήσης, η άδεια χρήσης αναφέρεται ρητώς. Χρηματοδότηση • Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό έχει αναπτυχθεί στα πλαίσια του εκπαιδευτικού έργου του διδάσκοντα. • Το έργο «Ανοικτά Ακαδημαϊκά Μαθήματα στο Ανώτατο Εκπαιδευτικό Ίδρυμα Πειραιά Τεχνολογικού Τομέα» έχει χρηματοδοτήσει μόνο την αναδιαμόρφωση του εκπαιδευτικού υλικού. • Το έργο υλοποιείται στο πλαίσιο του Επιχειρησιακού Προγράμματος «Εκπαίδευση και Δια Βίου Μάθηση» και συγχρηματοδοτείται από την Ευρωπαϊκή Ένωση (Ευρωπαϊκό Κοινωνικό Ταμείο) και από εθνικούς πόρους. 2 1. Exercise A ......................................................................................................... 4 2. Exercise Β ......................................................................................................... 5 3. Exercise C ......................................................................................................... 6 4. Exercise D ......................................................................................................... 8 3 1. Exercise A Fill in the diagram below with the components of a mechatronics system 4 2. Exercise Β Fill in the boxes below as follows: Row A - the components of a mechatronics system, Rows b,c,d,e,f,g -the devices or methods used to support these components A b c d e f g 5 3. Exercise C Find the terms in the text that match the following definitions 1. A mechanical, optical, or electronic system that is used to maintain a desired output. 2. Processing the form or mode of a signal so as to make it intelligible to or compatible with a given device, such as a data transmission line, including such manipulation as pulse shaping, pulse clipping, digitizing, and linearizing. 3. A branch of engineering that incorporates the ideas of mechanical and electronic engineering into a whole, and, in particular, covers those areas of engineering concerned with the increasing integration of mechanical, electronic, and software engineering into a production process. 4. Something put into a system or expended in its operation to achieve output or a result, especially: 5. A microcomputer, microprocessor, or other equipment used for precise process control in data handling, communication, and manufacturing. 6. The information produced by a program or process from a specific input 7. One that activates, especially a device responsible for actuating a mechanical device, such as one connected to a computer by a sensor link. 8. A control system that appears to be self-regulating. Closed-loop systems employ feedback and a reference of correctness (norm or set point). Deviations from the norm are detected and corrections made in order to maintain a desired state in the system. 9. The return of a portion of the output of a process or system to the input, especially when used to maintain performance or to control a system or process. 10. An amplifier having high direct-current stability and high immunity to oscillation, generally achieved by using a large amount of negative feedback; used to perform analog-computer functions such as summing and integrating. 11. An electric device consisting of one or more turns of wire and typically having two terminals. An inductor is usually connected into a circuit in order to raise the inductance to a desired value. 12. The layout of an application's graphic or textual controls in conjunction with the way the application responds to user activity: 13. The amount of data that can be passed along a communications channel in a given period of time. 14. One that processes, especially an apparatus for preparing, treating, or converting material 15. Any of various instruments for comparing a measured property of an object, such as its shape, color, or brightness, with a standard. 16. An interface found on some PIC microcontrollers It allows 8-bit asynchronous bidirectional data transfer between the PIC and external devices, such as other microcontrollers or personal computers. 17. A serial interface that can transfer data at up to 480 million bits per second and connect up to 127 daisy-chained peripheral devices 18. A device, usually electronic, which detects a variable quantity and measures and converts the measurement into a signal to be recorded elsewhere. 6 19. A portion of a program that carries out a specific function and may be used alone or combined with other modules of the same program. 20. The process of establishing target distance. 21. A surveying technique in which a region is divided into a series of triangular elements based on a line of known length so that accurate measurements of distances and directions may be made by the application of trigonometry. 22. Computer programming instructions that are stored in a read-only memory unit rather than being implemented through software. 23. A motor that rotates in short and essentially uniform angular movements rather than continuously; typical steps are 30,45, and 90°; 24. The restriction of an observable quantity, such as energy or angular momentum, associated with a physical system, such as an atom, molecule, or elementary particle, to a discrete set of values. 25. A commonly used technique for controlling power to inertial electrical devices, made practical by modern electronic power switches. Pulse-width modulation uses a rectangular nulse wave whose pulse width is modulated resulting in the variation of the average value of the waveform. 26. A device used to transfer electric energy from one circuit to another, especially a pair of multiply wound, inductively coupled wire coils that effect such a transfer with a change in voltage, current, phase, or other electric characteristic. 27. The fineness of detail that can be distinguished in an image, as on a video display terminal. 28. The appearance of jagged distortions in curves and diagonal lines in computer graphics because the resolution is limited or diminished OR the static distortion in digital sound caused by a low sampling rate. 29. An electronic amplifier (typically an operational amplifier) whose pain can be controlled by external digital or analog signals. 30. To convert (data) from fixed-point notation to floating-point notation. 7 4. Exercise D Using information from the text (and possibly of your own), make a paragraph of your own describing what a mechatronics system is. 8