* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Martin Fajkus Faculty of applied informatics Tomas Bata University
List of special economic zones wikipedia , lookup
Marginal utility wikipedia , lookup
Chicago school of economics wikipedia , lookup
Choice modelling wikipedia , lookup
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Marginalism wikipedia , lookup
Economic calculation problem wikipedia , lookup
Supply and demand wikipedia , lookup
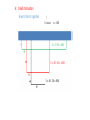
Some Economic applications of one variable functions. Martin Fajkus Faculty of applied informatics Tomas Bata University in Zlin A: Small motivation How to fence a garden ! S = 𝑚𝑎𝑥 c = 100 S = 5 · 90 = 450 S = 30 · 40 = 1200 S = 40 · 20 = 800 A: Small motivation How to fence a garden ! S = 𝑚𝑎𝑥 c = 100 S = 𝑎. 𝑏 c = 2𝑎 + 𝑏 = 100 𝑏 = 100 − 2𝑎 S = 𝑎. (100 − 2𝑎) S = 100𝑎 − 2𝑎2 ! S ´ = 100 − 4𝑎 = 0 𝑎 = 25 𝑏 = 100 − 2.25 𝑏 = 50 Smax = 25·50 = 1250 B: Economic applications I. Basic functions of economic analysis I. A. – utility function I. Basic functions of economic analysis I. A. – utility function; surplus Consumer surplus I. Basic functions of economic analysis Co-ordinate axes x-axis ⟷ x (or q) – QUANTITY y-axis ⟷ p – PRICE I. B. – demand and supply Demand p = d(x) ⟷ Supply x = D(p) Usually decreasing: With higher price people want to buy less. p = s(x) ⟷ x = S(p) Usually increasing: With higher price producers want to produce more. Demand function (copies marginal utility of the buyer) Market equlibrium; surplus and shortage supply demand I. Basic functions of economic analysis I. C. – costs, revenue; profit FIXED VARIABLE TOTAL COSTS FC VC(x) TC(x) = FC + VC(x) REVENUE FR VR(x) = p.x TR(x) = FR + VR(x) PROFIT FP VP TP(x) = TR(x) − TC(x) AVERAGE 𝐴𝐶 = 𝑇𝐶 𝑥 𝐴𝑅 = 𝑇𝑅 𝑥 𝐴𝑃 = 𝑇𝑃 𝑥