* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Wound Management - Dermatology Research Centers
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
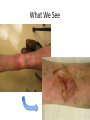
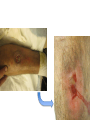
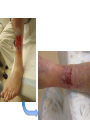
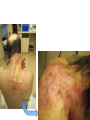
Dermatology Wound Clinic Jessica Scanlon, MD October 9, 2014 Who We Are • Physicians – Vince Li – Jessica Scanlon – Bill Tsiaras • Jen Elliott, PA-C • Nursing staff – MAs: Koravee, Tina – Triage: Mary – Scheduling: Janelle Trotman (used to be DaLisa) What We Do • Management of chronic wounds – Wounds lasting longer than 6 weeks – Frequent wounds – Pts with a history of chronic wounds – Complex wounds Conditions We Treat • The 3 big chronic wounds: – Venous leg ulcers – Diabetic foot ulcers – Arterial ulcers • Complex dermatologic conditions – – – – – – – – – Pyoderma gangrenosum Morphea Radiation dermatitis Vasculitis Infection NLD Calciphylaxis Tumors Etc… What We See Chronic Wounds • Wound management is complex • Requires frequent wound and dressing reassessment How Do We Operate • Team approach – Everyone has an important role in wound care • Important team players – – – – – – Patients: Age, comorbidities, ability to manage ADLs Families, friends: Complicated and complicating VNA, home health aides, hospice care Other wound centers PCPs, other specialties (vascular, plastics, ortho, onc) Dermatology: Office manager, MAs, triage, PA, MDs Managing Comorbidities • A chronic wound is a systemic disease – affected by a host of other factors – – – – – – – – – – – – – – Chronic disease Venous and/or arterial insufficiency Diabetes Neurologic defects Psychiatric disturbance Immunodeficiency Nutritional deficiency Medications Blood disorders, hypercoagulability Advanced age Allergy Pressure, infection, edema Smoking, alcohol, illicit drugs Others… Managing Pt Expectations • Ulcers have a big impact on QOL – Pain – Activity level, mobility – Time of dressing changes – Pt’s rely more heavily on others – Showering, swimming • Pt’s expect ulcers to heal quickly, painlessly, and with a minimum of trouble Choosing Appropriate Wound Dressings • Assessment of the wound/milieu – – – – – Moisture balance Inflammation Necrotic debris, crusting Bacterial bioburden (odor, drainage) Quality of the skin (ACD, xerosis, stasis, etc) • Comorbid factors – – – – Ease of dressing changes Pain Is the person changing the dressings making things worse? Dressing availability, cost Tools • Dressings • Debridement – Sharp debridement, collagenase • Compression • Topical agents – Regranex • Bio-Engineered Grafts – OASIS, Apligraf, Dermagraft, EpiFix • Antiseptic measures Maintaining the Moisture Balance Tegaderm (film) Duoderm (hydrocolloid) Aquacel (hydrofiber) Allevyn foam cavity dressing (foam) Antiseptic Dressings Compression Wound Clinic • Dressings taken down, wound cleaned with NS • EMLA – 15 minutes • Pt is evaluated, wound assessed – Measure the wound – Debridement – Cultures – Skin substitute if necessary – Wounds redressed Wound Clinic • Much of the work is done outside of clinic, by support staff – – – – – – – – PA’s, communicating with pharmacies Communicating with VNA or other wound care providers Managing supplies, compression pumps Ordering skin substitutes and obtaining them from the blood bank Providing OTC wound supply resources Managing cultures, biopsy results, labs Managing billing issues Managing pt concerns and expectations Care Coordination • • • • VNA services Medical supply ordering HBOT Medication/Dressing PAs – Regranex, collagenase, grafts • Physical therapy services – Lymphedema massage • Equipment – Wound VAC – Compression boots • Referrals – Vascular – Plastics – Renal, other medicine services Logistics • Scheduling – Urgent issues – All others go through our scheduler • Days – Thursdays AM/PM, Vince monthly – Bill Wednesdays • Location – 221 Longwood • Inpatient consult service