* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stabilization Policies
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Monetary policy wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Supply-side economics wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
Early 1980s recession wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
2008–09 Keynesian resurgence wikipedia , lookup
Post-war displacement of Keynesianism wikipedia , lookup
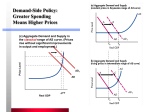
Students will explain the operations and impact of fiscal policy Students will distinguish between supply-side economics and fiscal policy Students will state the basic assumptions of monetary policy Fiscal Policy The Federal government’s attempt to stabilize the economy through taxing and government spending Keynesian Economics (demand-side economics) The theory that the federal government should increase or decrease aggregate demand to achieve economic goals (such as lowering unemployment) Examples 1932 – Franklin D. Roosevelt instituted his New Deal program to try and restore the economy. This was an expansionary policy that paid people to build highways, parks, schools, etc. The objective was to create jobs using public works projects 2001 – George Bush proposed and signed into law tax cuts to stimulate the economy followed by a tax rebate stimulus 2009 – the Obama administration stimulus package The Keynesian Framework Multiplier Change in overall spending caused by a change in investment spending Accelerator Change in investment spending caused by a change in overall spending The role of government Government should step in to offset changes in investment sector spending Automatic stabilizers Programs that automatically trigger benefits if changes in the economy threaten income Unemployment insurance Insurance that workers who lose their jobs through no fault of their own can collect for a limited amount of time Fiscal policy and aggregate demand When aggregate demand is very low the government can increase spending to increase aggregate demand Public works projects Limitations of Fiscal Policy Many times the government only uses the automatic stabilizers due to budgetary concerns Supply-side economics Smaller role for government Policies designed to stimulate output and lower unemployment by increasing production rather than demand Reduces governments role – reduced government agencies, deregulation, etc Lower federal taxes Allows individuals and businesses to keep more money which encourages people to work harder, be more productive, and spend more money Laffer Curve Graph that shows that lower tax rates will stimulate higher tax revenues Supply-side policies and aggregate supply Quantities produced at different possible prices Limitations of supply side policies Not enough experience with these policies and really know how they affect the economy Used more to promote economic growth than to fix economic instability Monetarism Interest Rates and Inflation A doctrine that places primary importance on the role of money and its growth Wage-price controls Regulations that make it illegal for businesses to raise wages or prices without permission from the government Monetary policy and unemployment Monetarist will agree that an attempt to lower unemployment by expanding the money supply is only a temporary solution and will cause other economic problems such as inflation.