* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 17 Economic Policymaking
Edmund Phelps wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Participatory economics wikipedia , lookup
Monetary policy wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Italy under fascism wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Keynesian economics wikipedia , lookup
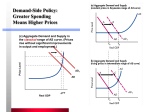
Chapter 17 Economic Policymaking Capitalism • Private individuals own the principal means of production • Prices and wages determined by Supply and Demand • “Free Market” = no government intervention of economy “It’s the economy, Stupid.” • Economic conditions drive voting behavior • Democrats = priority is to decrease unemployment • Republicans = priority is to decrease inflation Unemployment • Those people seeking work but unable to find it • Compiled by Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) via monthly surveys of 60,000 households • New jobs must be ~125,000/month just to keep pace with new workers • “Discouraged workers” = given up job hunt or taken part-time jobs Underemployment Rate • Unemployment Rate + Discouraged workers rate Inflation • Increase in prices for goods and services • BLS complies Consumer Price Index (CPI) by measuring the change in a fixed basket of goods and services (80,000) History • 1789-1929: Laissez-faire • 1929-present: regulatory and activist • 2 Tools to influence economy: • Monetary Policy and Fiscal Policy Monetary Policy • Control over money supply held in private hands • Federal Reserve Board – Prime % rate – Sells Bonds – Sets deposit reserve levels • These can influence expansion/contraction of the money supply Fiscal Policy • Federal Budget to influence economy • Taxing, Spending, Borrowing • Keynesian Economic Theory vs. Supply-Side Economics Keynesian Theory • Government spending stimulates the economy by creating demand for goods and services • “Pump-Priming” (New Deal/FDR) • Favored by Democrats • Considers deficit spending allowable, even necessary at times. Supply-Side Economics • Key task of policy is to stimulate supply, not demand • First adopted under Reagan, favored by Republicans • Lowering tax rates, de-regulating businesses, and decreasing government spending Regardless of strategy … • The concept of a free market economy / passive government re: economy is now virtually gone … • Government’s responsibility to use fiscal policy to control/influence the economy Then why is it so hard to control the economy? • Policies are slow to enact • “Uncontrollable expenditures” limit fiscal options • Free Enterprise system / philosophy limits government actions • Government spending / influence relatively small compared to billions of economic decisions made by consumers and business Arenas of Economic Policymaking Business Policy • Protectionism • Anti-Trust Policy –Preserve competition Consumer Policy • FDA • CPSC • FTC –To prevent harm to consumers Labor Policy • NLRB –To protect workers