* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
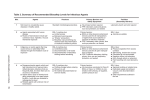
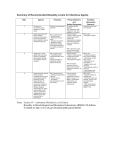
Download Summary of Recommended Biosafety Levels for Infectious Agents
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Summary of Recommended Biosafety Levels for Infectious Agents BSL 1 2 Agents Practices Not known to consistently cause diseases in healthy adults Standard microbiological practices • BSL-1 practice plus: • Limited access • Biohazard warning signs • “Sharps” precautions • Biosafety manual defining any needed waste decontamination or medical surveillance policies BSL-2 practice plus: • Controlled access • Decontamination of all waste • Decontamination of laboratory clothing before laundering • Agents associated with human disease Routes of transmission include percutaneous injury, ingestion, mucous membrane exposure 3 Indigenous or exotic agents that may cause serious or potentially lethal disease through the inhalation route of exposure 4 • • • Dangerous/exotic agents which post high individual risk of aerosol-transmitted laboratory infections that are frequently fatal, for which there are no vaccines or treatments Agents with a close or identical antigenic relationship to an agent requiring BSL-4 until data are available to redesignate the level Related agents with unknown risk of transmission BSL-3 practices plus: • Clothing change before entering • Shower on exit • All material decontaminated on exit from facility Primary Barriers and Safety Equipment • • No primary barriers required. PPE: laboratory coats and gloves; eye, face protection, as needed Primary barriers: • BSCs or other physical containment devices used for all manipulations of agents that cause splashes or aerosols of infectious materials • PPE: Laboratory coats, gloves, face and eye protection, as needed Primary barriers: • BSCs or other physical containment devices used for all open manipulations of agents • PPE: Protective laboratory clothing, gloves, face, eye and respiratory protection, as needed Primary barriers: • All procedures conducted in Class III BSCs or Class I or II BSCs in combination with fullbody, air-supplied, positive pressure suit Facilities (Secondary Barriers) Laboratory bench and sink required BSL-1 plus: • Autoclave available BSL-2 plus: • Physical separation from access corridors • Self-closing, double-door access • Exhausted air not recirculated • Negative airflow into laboratory • Entry through airlock or anteroom • Hand washing sink near laboratory exit BSL-3 plus: • Separate building or isolated zone • Dedicated supply and exhaust, vacuum, and decontamination systems • Other requirements outlined in the text BMBL 5th Edition Classification of Infectious Microorganisms by Risk Group Risk Group Classification NIH Guidelines for Research involving Recombinant DNA Molecules World Health Organization Laboratory Biosafety Manual 3rd Edition Risk Group 1 Agents not associated with disease in healthy adult humans. Agents associated with human disease that is rarely serious and for which preventive or therapeutic interventions are often available (No or low individual and community risk) A microorganism unlikely to cause human or animal disease. (Moderate individual risk; low community risk) A pathogen that can cause human or animal disease but is unlikely to be a serious hazard to laboratory workers, the community, livestock or the environment. Laboratory exposures may cause serious infection, but effective treatment and preventive measures are available and the risk of spread of infection is limited. (High individual risk; low community risk) A pathogen that usually causes serious human or animal disease but does not ordinarily spread from one infected individual to another. Effective treatment and preventive measures are available. Risk Group 2 Risk Group 3 Risk Group 4 Agents associated with serious or lethal human disease for which preventive or therapeutic interventions may be available (high individual risk but low community risk). Agents likely to cause serious or lethal human disease for which preventive or therapeutic interventions are not usually available (high individual risk and high community risk). (High individual and community risk)A pathogen that usually causes serious human or animal disease and can be readily transmitted from one individual to another, directly or indirectly. Effective treatment and preventive measures are not usually available.3 BMBL 5th Edition