* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IOW Dementia MUR Steve Bleakley Nov 2010
Survey
Document related concepts
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of neuraminidase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of ACE inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Atypical antipsychotic wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
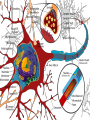
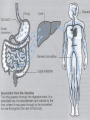
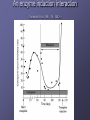
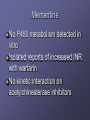
Drug interactions in dementia Stephen Bleakley Locality Lead Pharmacist November 2010 [email protected] Aims of talk Refresher on some pharmacology ADME Absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion Focus on P450 enzyme system Overview of interactions relating to Acetylcholinergics Antipsychotics Antidepressants Few others Why worry? BMJ 2004: 329; 15-19 6-7% of hospital admissions related to adverse drug reactions Drug interactions account for 1-2% 0.13% are fatal (US data) Around 70% considered avoidable Estimated NHS costs £500million Classifying drug interactions Pharmacodynamic – the effects of the drug on the body Pharmacokinetics – the way the body effects the drug over time (ADME) Drug administration Drug metabolism 1 Substrate – a drug which is metabolised by that enzyme Enzyme induction – some drugs increase the activity of the liver enzymes (1-2 weeks) Enzyme inhibition – some drugs reduce the activity of the liver enzymes (usually occurs over 1-2 days) Drug metabolism 2 Cytochrome P-450 enzymes Over 40 different enzymes 1A2, 2D6, 2C9 and 3A4 especially important in psychiatry Genetic polymorphism can occur An enzyme induction interaction Transplant Proc 1984, 16: 1642-5 At a glace guide to the P450 enzyme system Isoenzyme Inhibitor Inducer Substrate CYP 1A2 Ciprofloxacin Fluvoxamine Grapefruit juice Clarithromycin Erythromycin Tobacco Smoke Clozapine Duloxetine Olanzapine Tricyclic antidepressants CYP 2C9 Fluconazole Fluoxetine Fluvoxamine Cranberry Juice Diclofenac Gliclazide NSAIDs Trimethoprim Warfarin CYP2D6 (genetic polymorphism) Bupropion Duloxetine Fluoxetine Paroxetine Sertraline (dose dependent) Ciprofloxacin Donepezil Galantamine Clozapine Risperidone Tricyclic antidepressants Venlafaxine CYP3A4 Amiodarone Grapefruit juice Erythromycin Clarithromycin Fluconazole Carbamazepine St John’s Wort Aripiprazole Buspirone Calcium Channel Blockers Digoxin Haloperidol Donepezil Galantamine Benzodiazepines Carbamazepine Methadone Fentanyl Quetiapine Simvastatin Zopiclone Comparison interactions of the acetylcholinesterases Rivastigmine No significant CYP interactions Donepezil and Galantamine CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 inhibitors, - erythromycin - fluoxetine CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 inducers, - carbamazepine - St John’s Wort Compiled from SPCs; Grossberg GT et al., Int. J. Geriat. Psychiatry 2000; 15, 242-247 Pharmacodynamic interactions Think how the drug works What may oppose its actions What side effects are known Do co-prescribed drugs have similar side effects Anticholinergic effects Anticholinergic drugs can oppose the effects of Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors Class Anticholinergics Tricyclic antidepressants Examples Procyclidine, orphenadrine, trihexyphenidyl Amitriptyline, nortriptyline, imipramine, clomipramine Antipsychotics (not all) Chlorpromazine, clozapine, flupentixol, zuclopentixol Antimuscarinics for incontinence Oxybuyynin, tolterodine Pharmacodynamic interactions Co-prescribed drugs have similar side effects. Consider the potential pharmacodynamic interactions: Donepezil + Procyclidine Rivastigmine + fluoxetine Donepezil + atenolol Donepezil + NSAIDs Rivastigmine patches Windbland B et al. Int J of Geriatr Psychiatry 2007; 22: 456-467 Improved tolerability compared against rivastigmine oral capsules No comparative data against donepezil or galantamine yet Probably reduced risk of additive adverse reactions Clinical relevance Baxter K (ed), Stockley’s Drug Interactions. [online] London: Pharmaceutical Press <http://www.medicinescomplete.com/> (assessed January 2010) Clinical significance often unknown due to limited data Erythromycin + galantamine 10% increase in levels Ketoconazole + donepezil 30% increase in levels Paroxetine increases galantamine by 40% Memantine No P450 metabolism detected in vitro Isolated reports of increased INR with warfarin No kinetic interaction on acetylchinesterase inhibitors Adverse effects Antipsychotic EPSE Raised prolactin Weight Diabetes gain Raised lipids QT prolongati on Haloperidol +++ +++ + + - +++ Zuclopenthixol +++ +++ ++ ++ + ? Flupenthixol ++ +++ ++ ++ + + Chlorpromazine ++ +++ ++ ++ + ++ Sulpiride + +++ + -? -? + Amisulpiride + +++ + - -? + Risperidone + +++ ++ ++ + + Paliperidone + +++ ++ ++? + +? Olanzapine - + +++ +++ +++ - Quetiapine - - ++ ++ ++ ++ Aripiprazole - - + - - - Clozapine - - +++ +++ +++ + Antidepressant interactions Fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline and duloxetine Inhibitors at CYP2D6 Increases levels of TCAs Some antipsychotics Serotonin syndrome MAOIs Tyramine interactions Lithium interactions Thiazides increase lithium levels NSAIDs increase lithium levels Do not use p.r.n NSAIDs ACE inhibitors increase lithium levels Dehydration and salt free diet increase lithium levels Carbamazepine Major inducer of 3A4 isoenzyme Increases the clearance of: many antidepressants, some antipsychotics, benzodiazepines, oestrogens, erythromycin, SSRIs and methadone Causes enzyme auto-induction Drug – disease interactions Liver disease Renal disease Cardiac disease Epilepsy Type of dementia Conclusions Interactions to look out for Anticholinergics with acetylchonesterase inhibitors 2D6 and 3A4 inhibitors and inducers with donepezil and galantamine St Johns wort and carbamazepine with anything Drugs which worsen or exacerbate side effects Lithium with any drug which alters renal or electrolyte balance Thank you Any questions?