* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download URINARY TRACT INFECTION
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
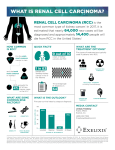
Renal Pathology Introduction: • 150gm: each kidney • 1700 liters of blood filtered 180 L of G. filtrate 1.5 L of urine / day. • Kidney is a retro-peritoneal organ • Blood supply: Renal Artery & Vein • One half of kidney is sufficient – reserve • kidney function: Filtration, Excretion, Secretion, Hormone synthesis. Kidney Location: Kidney Anatomy: Renal Pathology Outline • Glomerular diseases: Glomerulonephritis • Tubular diseases: Acute tubular necrosis • interstitial diseases: Pyelonephritis • Diseases involving blood vessels: Nephrosclerosis • Cystic diseases • Tumors Clinical Syndromes: • Nephritic syndrome. – Oliguria, Haematuria, Proteinuria, Oedema. • Nephrotic syndrome. – Gross proteinuria, hyperlipidemia, • Acute renal failure – Oliguria, loss of Kidney function - within weeks • Chronic renal failure. – Over months and years - Uremia Introduction • Functions of the kidney: – excretion of waste products – regulation of water/salt – maintenance of acid/base balance – secretion of hormones • Diseases of the kidney – glomeruli – tubules – interstitium – vessels Abnormal findings • Azotemia: BUN, creatinine • Uremia: azotemia + more problems • Acute renal failure: oliguria • Chronic renal failure: prolonged uremia Nephrotic syndrome Nephritic syndrome • Massive proteinuria • Hematuria • Hypoalbuminemia • Oliguria • Edema • Azotemia • Hyperlipidemia/-uria • Hypertension Glomerular diseases – Nephrotic syndrome • Minimal change disease • Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis • Membranous nephropathy – Nephritic syndrome • Post-infectious GN • IgA (immune) nephropathy Nephrotic Syndrome • Massive proteinuria • Hypoalbuminemia • Edema • Hyperlipidemia • Lipiduria Causes • Adults: systemic disease (diabetes) • Children: minimal change disease • Characterized by loss of foot processes • Good prognosis Minimal change disease Minimal change disease Normal glumerular structure Minimal change disease Normal glomerulus Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis • Primary or secondary • Some (focal) glomeruli show partial (segmental) hyalinization • Unknown pathogenesis • Poor prognosis Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis Membranous Glomerulonephritis • Autoimmune reaction against unknown renal antigen • Immune complexes • Thickened GBM • Subepithelial deposits Membranous glomerulonephritis Nephritic Syndrome • Hematuria • Oliguria, azotemia • Hypertension Causes • Post-infectious GN, IgA nephropathy • Immunologically-mediated • Characterized by proliferative changes and inflammation Post-Infectious Glomerulonephritis • Child after streptococcal throat infection • Immune complexes • Hypercellular glomeruli • Subepithelial humps Post-infectious glomerulonephritis IgA Nephropathy • Common! • Child with hematuria after (URI) Upper Respiratory Infection • IgA in mesangium • Variable prognosis IgA nephropathy URINARY TRACT INFECTION • Tubular and interstitial diseases – Inflammatory lesions • pyelonephritis Pyelonephritis • Invasive kidney infection • Usually ascends from UTI • Fever, flank pain • Organisms: E. coli, Proteus Urinary Tract Infection • Women, elderly • Patients with catheters or mal-formations • Dysuria, frequency • Organisms: E. coli, Proteus Acute pyelonephritis with abscesses Pyelonephritis Cellular cast Chronic pyelonephritis Drug-Induced Interstitial Nephritis • Antibiotics, NSAIDS • IgE and T-cell-mediated immune reaction • Fever, eosinophilia, hematuria • Patient usually recovers • Analgesic nephritis is different (bad) Drug-induced interstitial nephritis Acute Tubular Necrosis • The most common cause of ARF! • Reversible tubular injury • Many causes: ischemic (shock), toxic (drugs) • Most patients recover Acute tubular necrosis Benign Nephrosclerosis • Found in patients with benign hypertension • Hyaline thickening of arterial walls • Leads to mild functional impairment • Rarely fatal Benign nephrosclerosis Malignant nephrosclerosis • Arises in malignant hypertension • Hyperplastic vessels • Ischemia of kidney • Medical emergency Malignant Hypertension • 5% of cases of hypertension • Super-high blood pressure, encephalopathy, heart abnormalities • First sign often headache, scotomas • Decreased blood flow to kidney leads to increased renin, which leads to increased BP! • 5y survival: 50% Malignant hypertension Adult Polycystic Kidney Disease • Autosomal dominant • Huge kidneys full of cysts • Usually no symptoms until 30 years • Associated with brain aneurysms. Adult polycystic kidney disease Childhood Polycystic Kidney Disease • Autosomal recessive • Numerous small cortical cysts • Associated with liver cysts • Patients often die in infancy Childhood polycystic kidney disease Medullary Cystic Kidney Disease • Chronic renal failure in children • Complex inheritance • Kidneys contracted, with many cysts • Progresses to end-stage renal disease • Tumors – Renal cell carcinoma – Bladder carcinoma Renal Cell Carcinoma • Derived from tubular epithelium • Smoking, hypertension, cadmium exposure • Hematuria, abdominal mass, flank pain • If metastatic, 5y survival = 5% Renal cell carcinoma Bladder Carcinoma • Derived from transitional epithelium • Present with painless hematuria • Prognosis depends on grade and depth of invasion • Overall 5y survival = 50% Bladder carcinoma Thank you