* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quality Of Service
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
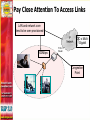
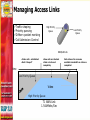
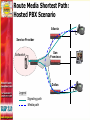
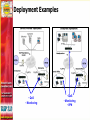
Dave Martin Vice President, Product Management [email protected] 408.351.7209 Agenda Challenges for converged networks Quality of Service Monitoring VoIP performance Troubleshooting Solutions and best practices Deployment examples Service Provider Enterprise Wrap-up/summary Quality Of Service Why Is It Necessary? “Becauszzzz wit_o_t it _sers w__l be unha_py!” PSTN has set the bar - VoIP as a replacement technology must offer the same quality experience Users will tradeoff voice quality for mobility - not true for fixed line services VoIP has very stringent jitter, latency and packet loss requirements…best effort IP forwarding is insufficient Ensuring A High Quality Voice Experience: Design Considerations Prioritize voice over data traffic Take advantage of DiffServ routing if available in the network… but remember… TOS bit setting is NOT traffic management !! Implement traffic shaping Provide call admission control Route media shortest path Pay Close Attention To Access Links LAN and network core tend to be over-provisioned OC-x MultiGigabit 100Mbps T-1/E-1 Router Congestion Point Managing Access Links Traffic shaping Priority queuing Diffserv packet marking Call Admission Control High Priority Queue Low Priority Queue WAN/LAN Link •Video calls established •Data “shaped” •New calls are blocked •Data not starved completely time Low Priority Queue Video High Priority Queue T1 WAN Link 1.544Mbits/Sec Data allowed to consume available bandwidth as calls are completed Route Media Shortest Path: Hosted PBX Scenario Atlanta Service Provider San Francisco Softswitch Dallas Legend Signaling path Media path VoIP Monitoring Issues Distributed nature of IP networking means no natural demarcation point for problem resolution I just had a poor quality call…...but why? Difficult to monitor long term call performance and identify consistently poor performers Create Demarcation Points Signaling Media VoIP Manager Softswitch or IP PBX IP Phone A Location #3 Location #1 Location #2 IP network B C D IP Phone Mean Opinion Score (MOS) provides a simple listening quality scale the represents the user experience Monitoring at points A, B, C and D provides a demarcation point between LAN and WAN Use Call Quality Statistics To Isolate Network Problems Common causes of jitter: • Ethernet link set at half duplex • Ethernet link set to autonegotiate • Congestion in upstream router Provide Proactive Support Trend analysis at the network level can spot persistent problems Set quality thresholds for advanced notification Deployment Examples • QoS • Monitoring • QoS • Monitoring • VPN Best Practices Summary Quality of Service Implement prioritization, traffic shaping, call admission control Route calls shortest path to minimize jitter, latency, and packet loss Monitoring Create demarcation points Build quality monitoring into the network Use tools that report on the user experience and send proactive notification of VoIP quality problems Thank You! Contact : Dave Martin Vice President, Product Management [email protected] 408.351.7209