* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Operations research wikipedia , lookup
Project management wikipedia , lookup
Strategic management wikipedia , lookup
High-commitment management wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable management wikipedia , lookup
Operations management wikipedia , lookup
Environmental resource management wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem-based management wikipedia , lookup
Management consulting wikipedia , lookup
Investment management wikipedia , lookup
International Council of Management Consulting Institutes wikipedia , lookup
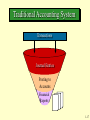
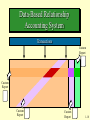
Fourth Edition Cost Management ACCOUNTING AND CONTROL HANSEN & MOWEN 1-1 Task Force Clip Art included in this electronic presentation is used with the permission of New Vision Technology of Nepean Ontario, Canada. 1-2 Introduction to Cost Management Prepared by Douglas Cloud Pepperdine University 1-3 Objectives 1. List the similarities and differences between After studying this financial accounting and cost management. chapter, you should 2. Identify the current factors be able to: affecting cost management. 3. Discuss the importance of the accounting system for internal and external reporting. 4. Explain the need for today’s cost accountant to acquire cross-functional expertise. 1-4 Objectives 5. Describe how management accountants function within an organization. 6. Understand the importance of ethical behavior for management accounts. 7. Identify the thee forms of certification available to internal accountants. 1-5 Financial Accounting Versus Cost Management Financial accounting is devoted to providing information for external users; these users include investors, government agencies, and banks. Cost management identifies, collects, measures, classifies, and reports information that is useful to managers in costing (determining what something costs), planning, controlling, and decision making. 1-6 Financial Accounting Versus Cost Management Cost accounting attempts to satisfy costing objectives for both financial and management accounting. Management accounting is concerned specifically with how cost information and other financial and nonfinancial information should be used for planning, controlling, and decision making. 1-7 Current Factors Affecting Cost Management Global Competition • The new competitive environment has increased the demand not only for more cost information but also for more accurate information. • Vastly imported transportation and communication has led to a global market for many manufacturing and service firms. 1-8 Current Factors Affecting Cost Management Growth of the Service Industry As the traditional industries has declined in importance, the service sector of the economy has increased in importance. Deregulation of many services has increased competition in the service industry. 1-9 Current Factors Affecting Cost Management Advances in Information Technology Computers are used to monitor and control operations, which allows for a considerable amount of useful information to be collected and provided to management instantaneously. The emergence of electronic commerce which allows buyers and sellers to come together electronically. 1-10 Current Factors Affecting Cost Management Advances in Management Environment The theory of constraints is a method used to continuously improve manufacturing activities and nonmanufacturing activities. Just-in-time manufacturing is a demand-pull system that strives to produce a product only when it is needed and only in the quantities demanded by customers. Computer-integrated manufacturing is the automation of the manufacturing environment. 1-11 Current Factors Affecting Cost Management Customer Orientation Firms are concentrating on the delivery of value to the customer with the objective of establishing a competitive advantage. Companies must compete not only in technological and manufacturing terms but also in terms of the speed of delivery and response. 1-12 Current Factors Affecting Cost Management New Product Development Management recognizes that a high proportion of production costs are committed during the development and design stage of a new product. The requirement to control cost encourages the use of target costing and activity-based management. 1-13 Current Factors Affecting Cost Management Total Quality Management Continual improvement and elimination of waste are the two foundation principles that govern a state of manufacturing excellence. A philosophy of total quality management, in which managers strive to create an environment that will enable organizations to manufacture perfect products, has replaced the acceptable quality attitudes of the past. 1-14 Current Factors Affecting Cost Management Time as a Competitive Element Time is the crucial element in all phases of the value chain. Decreasing non-valueadded time appears to go hand-in-hand with increasing quality. 1-15 Current Factors Affecting Cost Management Efficiency While quality and time are important, improving these dimensions without corresponding improvements in financial performance may be futile, if not fatal. . 1-16 Traditional Accounting System Transactions Journal Entries Posting to Accounts Financial Reports 1-17 Data-Based Relationship Accounting System Transactions Custom Report Custom Report Custom Report Custom Report 1-18 Line and Staff Positions Line positions are positions that have direct responsibility for the basic objectives of an organization. Staff positions are positions that are supportive in nature and have only indirect responsibility for an organization’s basic objectives. 1-19 Partial Organization Chart, Manufacturing Company President Line Function Staff Function Production Vice-President Financial VicePresident Production Supervisor Machining Foreman Assembly Foreman Controller Internal Audit Cost Financial Treasurer Systems Ta x 1-20 Role of Controller and Treasurer Controller 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Financial reports SEC reporting Tax planning and reporting Performance reporting Internal auditing Budgeting Accounting systems and internal controls 1-21 Role of Controller and Treasurer Treasurer 1. Collection of cash 2. Monitoring of cash payments 3. Monitors cash availability 4. Short-term investments 5. Short and long-term borrowing 6. Issuing of capital stock 1-22 The Management Process Planning is the detailed formulation of future actions to achieve a particular end. Planning requires setting objectives and identifying methods to achieve those objectives. 1-23 The Management Process Controlling is the managerial activity of monitoring a plan’s implementation and taking corrective action as needed. Control Feedback is usually is information achieved that with canthe be use usedoftofeedback. evaluate or correct the steps being taken to implement a plan. 1-24 The Management Process Continuous improvement is required in a dynamic environment if a firm is to remain competitive or to establish a competitive advantage. 1-25 The Management Process Decision making is the process of choosing among competing alternatives. 1-26 Standards of Ethical Conduct for Management Accountants Competence: Management accountants have a responsibility to-1. Maintain an appropriate level of professional competence by ongoing development of their knowledge and skills. 2. Perform their professional duties in accordance with relevant laws, regulations, and technical standards. 3. Prepare complete and clear reports and recommendations after appropriate analysis of relevant and reliable information. 1-27 Standards of Ethical Conduct for Management Accountants Confidentiality: Management accountants have a responsibility to-1. Refrain from disclosing confidential information acquired in the course of their work except when authorized, unless legally obligated to do so. 2. Inform subordinates as appropriate regarding the confidentiality of information acquired in the course of their work and monitor their activities to ensure the maintenance of that confidentiality. 3. Refrain from using or appearing to use confidential information acquired in the course of their work for unethical or illegal advantage either personally or through a third party. 1-28 Standards of Ethical Conduct for Management Accountants Integrity: Management accountants have a responsibility to- Avoid actual or apparent conflicts of interest and advise all appropriate parties of any potential conflict. Refrain from engaging in any activity that would prejudice their ability to carry out their duties ethically. Refuse any gift, favor, or hospitality that would influence their actions. Refrain from either actively or passively subverting the attainment of the organization’s legitimate and ethical objectives. Continued 1-29 Standards of Ethical Conduct for Management Accountants Integrity: Management accountants have a responsibility to- Recognize and communicate professional limitations or other constraints that would preclude responsible judgment or successful performance of an activity. Communicate unfavorable as well as favorable information and professional judgments or opinions. Refrain from engaging in or supporting any activity that would discredit the profession. 1-30 Standards of Ethical Conduct for Management Accountants Objectivity: Management accountants have a responsibility to-1) Communicate information fairly and objectively. 2) Disclose fully all relevant information that could reasonably be expected to influence an intended user’s understanding of the reports, comments, and recommendations presented. 1-31 Professional Certifications CMA: One of the main purposes of the CMA was to establish management accounting as a recognized, professional discipline, separate from the profession of public accounting. CPA: The responsibility of a CPA is to provide assurance concerning the reliability of financial statements. CIA: The focus of the CIA is to recognize competency in internal auditing rather than external auditing as with the CPA. 1-32 The CMA Four areas emphasized on the exam: 1) Economics, finance, and management 2) Financial accounting and reporting 3) Management report, analysis, and behavioral issues 4) Decision analysis and information systems 1-33 End of Chapter 1-34 1-35