* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 11 - Lyme Disease
Bovine spongiform encephalopathy wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Bioterrorism wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Lyme disease wikipedia , lookup
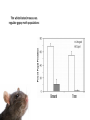
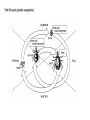
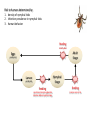
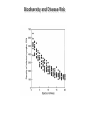
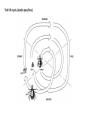
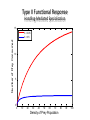
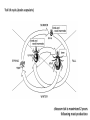
The Ecology of Lyme Disease oaks, moths, mice, gypsy moths, and lyme disease Gypsy Moth Defoliation (1975-2008) The white-footed mouse can regulate gypsy moth populations While gypsy moth populations have been down the incidence of Lyme disease has increased What is going on? Lyme Disease Biology Caused by the spirochete bacteria Borrelia burgdorferi Vectored by ticks (in California Ixodes pacificus) Vector: any agent that carries and transmits an infectious agent A Community of Borrelia Hosts western fence lizard dusky-footed woodrat white-footed mouse eastern chipmunk Target Hosts our best friends white-tail deer mom and dad Lyme Disease Symptoms Within a few days: Skin rash 3-30 days after tick bite Within days or weeks: Fatigue Chills Fever Headache Muscle and joint aches Swollen lymph nodes Bell’s Palsy (loss of muscle tone on one side of the face) Long-term neurological problems: Problems with concentration Short-term memory loss Severe arthritis and joint pain Erythema migrans (~70% cases) Lyme Disease History did it just appear in the 1970s? 1883: The first record of a condition like Lyme Disease 1921: Joint problems disease is associated with Ixodes scapularis ticks 1975: Cluster of cases of rashes and swollen joints in Lyme, Connecticut 1982: Borrelia burgdorferi is discovered by Dr. Willy Burgdorfer How do you show that a particular microbe causes a disease? Koch’s postulates To establish that an organism causes disease, is must be: 1. found in all cases of the disease examined, while absent in healthy organisms 2. prepared and maintained in a pure culture (some practical difficulties here) 3. capable of producing the original infection (some ethical difficulties here) 4. retrievable from an inoculated animal and cultured again Tick life cycle (Ixodes scapularis) Risk to humans determined by: 1. density of nymphal ticks 2. infection prevalence in nymphal ticks 3. human behavior feeding mostly deer Adult Stage Eggs uninfected Nymphal Stage Larvae uninfected feeding feeding one chance to pick up Borrelia infection before nymphal stage humans are at risk How Does the Host Community Affect Disease Risk disease risk = lyme disease cases Increased Disease Risk Decreased Disease Risk Amplification Adding a species to a community increases the total abundance of hosts for the pathogen, increasing the disease risk to the target host Dilution Adding a species to a community decreases the abundance of more competent hosts, decreasing the disease risk to the target host Each tick feeds only once per stage Feedings spent on poorly-competent hosts are wasted for the disease Competence (for hosts) The efficiency with which a host acquires and spreads a pathogen How Does the Host Community Affect Disease Risk disease risk = lyme disease cases White footed mice are a preferred host = more ticks White footed mice are a competent host = more infected ticks How Does the Host Community Affect Disease Risk disease risk = lyme disease cases Increased mammal diversity = more ticks, less ticks, who knows Increased mammal diversity = less infected ticks Biodiversity and Disease Risk Biodiversity and Disease Risk Tick life cycle (Ixodes pacificus) Reservoir competence Hosts differ in their efficiency at acquiring and spreading the Borrelia spirochete highly competent dusky-footed woodrat Neotoma fuscipes somewhat competent deer mouse Peromyscus maniculatus totally incompetent western fence lizard Sceloporus occidentalis The Lizard That Fights Lyme Disease Proteins found in the blood of S. occidentalis kill the Borrelia spirochete Tick life cycle (Ixodes pacificus) The Lizard That Fights Lyme Disease Prevalence of the Borrelia spirochete ≈ 30% - 60% Prevalence of the Borrelia spirochete ≈ 1% - 2% Does the Forest Community Affect Disease Risk? Does the Forest Community Affect Disease Risk? ? ? ? ? What about gypsy moths? Mast production, or masting, refers to the synchronous, episodic production of heavy seed crops by a population of plants Red oaks (Quercus rubra) mast every 3-5 years What are the ecological benefits of masting? Type II Functional Response Handling-Mediated Specialization 15 Number of Prey Consumed h = 0.05 h = 0.5 10 5 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Density of Prey Population 80 90 100 Tick life cycle (Ixodes scapularis) disease risk is maximized 2 years following mast production