* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Equilibrium
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
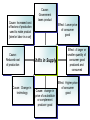
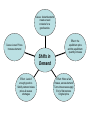
Combining Supply & Demand Balancing the Market -Combining the supply and demand schedules will create a balance. -Equilibrium is the point where supply & demand meet. -The market is stable at the equilibrium price. -To graph equilibrium combine the supply and demand graphs where they intersect is the equilibrium price. Disequilibrium Price Ceilings Price Floors -Occurs when quantity supplied and quantity demanded are not equal. -Excess demand occurs when quantity demanded is more than the quantity supplied. -Excess Supply occurs When the quantity Supplied is more than Quantity demanded. -a maximum price that can be legally charged for a good or a service. -these goods are seen by government As ‘essential’. -rent control is an example of how government tried to prevent inflation in housing -a minimum price for a good or service. -minimum wage is the minimum price an employer can pay a wage worker. -some commodities receive a price floor by state governments – milk. Cause: Increased cost of factors of production used to make product [steel or labor in a car] Cause: Reduced cost of production Cause: Change in technology Cause: Government taxes product Effect: Lower price of consumer good Shifts in Supply Cause: change in price of a substitute or complement producer good Effect: A larger or smaller quantity of consumer good produced and consumed Effect: Higher price of consumer good Cause: Advertisements create a need or desire for a good/service. Effect: the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity increase Cause: Lower Prices Increase demand Shifts in Demand Effect: Lack of enough goods to Satisfy demand raises prices & causes shortages Effect: When a fad Passes, excess demand Turns into excess supply End of fad restores Original price Signals that give producers and consumers information about the market Incentives to both buyer & sellers System is not flexible because determined by government Price based System Flexibility Rationing of goods can occur Because goal is to distribute wealth evenly, no incentives or signals to buyers or sellers. Centrally Planned System System is ‘free;’ it costs nothing to administer Great diversity of goods & services Shortages can occur Requires large bureaucracy to run Black markets can arise Fewer choices of goods






![[A, 8-9]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006655537_1-7e8069f13791f08c2f696cc5adb95462-150x150.png)






