* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Student Teaching Portfolio
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
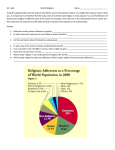
Multiculturalism in a Closed Minded World Turnar Kist Content Religions to be examined Hinduism Background Beliefs Holy days Sikhism Background Beliefs Holy days Islam Background Beliefs Holy days How to modify Conclusion Questions Religions Hinduism Sikhism Islam Hinduism Hinduism Majority of people in India and Nepal are Hindu Over 900 million members worldwide No single founder, no single scripture and no commonly agreed set of teachings Derived from river complex known as the Sindhu. Cultural, political and geographical origins. Of recent origin, yet its roots and formation go back thousands of years Henotheistic-one god, many representations. Ganges is holiest river. Hinduism- Beliefs 3 gods make up the Hindu triumvirate. Brahma (creator of universe), Shiva (destroyer of the universe) and Vishnu (protector and preserver of the universe) Atman- Eternal self. Real self beyond ego or false self. Often referred to as spirit or soul. Dharma- duty, virtue, morality and the power which upholds the universe and society. Hinduism-Beliefs Karma- Law that every action has an equal reaction either immediately or in the future. Both good and bad actions have reactions Samsara- Continuous cycle in which the soul is reborn over and over again according to the law of action and reaction-also called reincarnation Purushartha- Life has different goals according to a person’s stage in life and position in society. Hinduism-Beliefs The Vedas-sacred texts. Introduced by the Aryans Samhitas- Most ancient part consisting of hymns of praise to god. –similar to Psalms Brahmanas- Rituals and prayers to guide the priests in their duties. Aranyakas- Worship and meditation Upanishads- Mystical and philosophical teachings of hinduism. Hinduism-Worship Individual rather than communal. Involves making personal offerings to deity. Majority of homes have a shrine to one of the gods Does occur at temples-Central shrine is heart of worshipper and the tower represents the flight of the spirit to heaven. Hinduism-Worship 3 rites: Nitya- Performed daily and are offerings to the deities. Naimittika- Celebrations and festivals. Kamya- Highly desirable, but optional-pilgrimage. Kumbh Mela- Once every 12 years up to 10 million people bathe at Allahabad where the Ganges and Jumna combine. Hinduism-Holy days Diwali Festival of lights Most popular of South Asian festivals Celebrates victory of good over evil, light over darkness, and knowledge over ignorance. Fireworks are a big part of the festival. Sikhism Sikhism- Background Founded over 500 years ago. World’s fifth largest religion with over 20 million followers Founded by Guru Nanak and based on his teachings and of the 9 gurus who followed him Sikhism-Beliefs Monotheistic Stresses importance of doing good actions, rather than merely carrying out rituals Way to lead a good life is: Keep God in heart and mind at all times Live honestly and work hard Treat everyone equally Be generous to less fortunate Serve others People in the faith are members of the Khalsa. Sikhism-Beliefs Five vices: Lust Greed Worldly attachment Anger Pride The 5 Ks Kesh- uncut hair Kara- steel bracelet Kanga- Wooden comb Kaccha- Cotton underwear Kirpan- Steel sword Sikhism-Beliefs Kesh- Holiness and strength. Adoption of simple life and denial of pride in one’s appearance. Kara- Symbol of restraint and gentility. Symbol of god having no beginning or end. Kanga- Clean mind and body Kaccha- Symbol of chastity Kirpan- Can be anything from a few inches to three feet long. Symbolizes spirituality, defence of good, defence of weak, and the struggle against injustice. Sikhism- Beliefs Amrit Ceremony Similar to baptism. Take new names and wear the 5 Ks. Occurs as soon as they are old enough to understand the full commitment Gurdwara Place where Sikhs go for congregational worship. Presence of the Guru Granth Sahib which are the scriptures. No idols, statues, candles, or ritualistic devices Focus on reverence of scripture. All visitors must remove shoes and cover their heads before entering. Sikhism- Holy days Diwali Celebrates the release from prison of the 6th guru, Guru Hargobind. Festival of lights just as in Hinduism Gurpurbs Festivals that are associate with the lives of the Gurus. Important ones are birthdays of Guru Nanak and Guru Gobind Singh. Also important are martyrdoms of Guru Arjan and Guru Tegh Bahadur. Islam Islam- Background Means ‘submission to the will of God’. Second largest religion in the world-over 1 billion followers. Monotheistic- Allah Began over 1400 years ago in Mecca, Arabia. Gained many followers due to the accepting nature of the religion. Main 2 sects are Sunni and Shia. Split occurred because of the disagreement on who was supposed to be main leader after death of Muhammad. Islam- Beliefs Angels, holy books, prophets. Main prophets are Abraham, Moses, David, Jesus. Muhammad (peace be upon him) is the final prophet. Belief in Day of judgment and in predestination. Heart of the faith is obedience to Allah’s will. A believer can talk to Allah by praying and by reciting the Qur’an. Qur’an is the Muslim Holy Book. Islam- Beliefs Jihad- Struggle or effort. Is the inner struggle to live out the Muslim faith as well as possible. Struggle to defend Islam, with force if necessary Hijab- Means barrier or partition. Is the principle of modesty and includes behaviour as well as dress for men and women Most visible form is the head covering that women wear. In one school of thought, it refers to the complete covering of everything except the hands, face, and feet. A woman that wears a Hijab is called Muhaajaba. Niqab- Different than Hijab. Used to refer to the piece of cloth which covers the face. Women who wear it usually cover their hands as well. Other ways to cover oneself are the Burka, Al-Amira, Shayla, Khimar and Chador. Islam- Beliefs 5 Pillars: Shahadah- Sincerely reciting the Muslim profession of faith Salat- Performing ritual prayers in the proper way five times each day Zakat- Paying an alms tax to benefit the poor and needy Sawm- Fasting during month of Ramadan Hajj- Pilgrimage to Mecca Important because Islam regards it pointless to live life without putting that faith into action and practice. Proves they are putting their faith first. Islam- Beliefs Sharia: Comes from the Qur’an, Hadith (sayings and conduct of the prophet Muhammad), and fatwas (the ruling of Islamic scholars). Literally translates as a path to be followed. Muslims must believe in Allah. Strive for traits like humility and kindness. Actions must be related to the 5 pillars. Islam-Beliefs (Salaat) Allaahu Akbar (4x) Ashhadu an la ilaaha illaLah (2x) Ash Hadu anna Muhamadar rasuulullah (2x) Hayya’ alas Salaah (2x) Hayya’ ala Falaah (2x) [Fajr only: A-Salaatu Khayrun Mina-Naum (2x)] Qad qaamitis Salaah (2x) Allaahu Akbar (2x) Laa ilaaha illa-Lah God is the most great. I bear witness that there are not gods but God. I bear witness that Muhammad is the Messenger of God. Come to prayer. Come to felicity. [Prayer is better than sleep] Our prayers are now ready. Our prayers are now ready. God is the most great. There is no deity save God. Islam- Beliefs Worship occurs in a mosque Masjid is other word-means place of prostration No pictures or statues in the religion or the mosque. Women sit separately from the men out of modesty and to prevent any distraction. Islam- Holy Days Only 2 Muslim festivals set in Islamic Law: Eid ul Fitr (end of fasting and thanking Allah for help and strength throughout Ramadan) Eid ul Adha (4 days long. Remembers Abraham’s willingness to sacrifice his son when God ordered him to). Islam- Holy Days Ramadan Ninth month of the Islamic calendar when Muslims fast during daylight hours Important because Qur’an was first revealed during this month, gates of Heaven are open, gates of Hell are closed. Fasting in all areas-food, sleeping, sex and use of time. Taraweeh Prayers- Long night prayers that usually last for one and a half to two hours. I’tikaf- Going into seclusion during the last ten nights while praying and reading the Qur’an. How to modify for: Hinduism Be sure to assist students in doing good deeds for good Karma. Let them show their faith. Incorporate Hinduism into the lesson if it fits-example would be through a world religion class. How to modify for: Sikhism Modify rules so hair length and facial hair are not an issue. Although security is a major concern, the Kirpan is usually smaller when it is a younger Sikh, so it should not be an issue. Being kept in backpack can always be a modification How to modify for: Islam Allow for prayer time (my Catholic High School allowed the Muslim students to use the chapel to do their daily prayers) Allow students to wear their religious articles of clothing Ensure I know when Ramadan is to help the students commit to fasting and to be able to aid them during the month. How to modify for: All 3 Learn when religious days are-students will be excused if proper communication due to importance of these Holy Days Give opportunities for service Incorporate the histories and ideals into my lessons World religions classes So how do we fix this?! EDUCATE!!! We live in a culturally diverse world that is full of ignorance. If education does not occur, the ignorance will grow and so will the racism and lack of acceptance. I grew up in a diverse country and have experienced how little the differences actually are. We are all human beings, and we must learn to accept others for who they are and what they believe, and the best way to do this is learn about others and their religions. Resources http://www.bbc.co.uk/religion/religions/hinduism/ http://www.bbc.co.uk/religion/religions/islam/ http://www.bbc.co.uk/religion/religions/sikhism/ http://www.religionfacts.com/islam/branches Brittanica- Hinduism Britannica- Sikhism Questions?